보건의료전문직교육에서 학생선발 도구와 학생 다양성: 다기관 연구 (Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2023)
Selection tools and student diversity in health professions education: a multi‑site study
S. Fikrat‑Wevers1 · K. M. Stegers‑Jager1 · P. M. Afonso2,3 · A. S. Koster4 · R. A. Van Gestel4 · M. Groenier5 · J. H. Ravesloot6 · A. Wouters7,8 · W. W. Van Den Broek1 · A. M. Woltman1

소개
Introduction
의과대학 및 기타 보건 전문직 교육(HPE) 학교는 자격을 갖춘 학생을 선발할 뿐만 아니라 이들이 미래에 복무하게 될 다양한 사회를 반영하는 학생 집단을 만들어야 할 책임이 있습니다(General Medical Council, 2015). 형평성과 공정성 문제 외에도 다양한 의료 인력은 의료 서비스 제공자의 문화적 역량을 향상시키는 것 외에도, 다양한 인구 집단에 대한 양질의 의료 서비스에 대한 접근성을 높이고 균등화하는 데 중요합니다(Cohen et al., 2002; Morgan et al., 2016). 그러나 학부 HPE 프로그램의 선발 절차는 지원자 하위 그룹에 선발 기회가 불균등하게 분배되기 때문에 학생의 다양성이 영향을 받을 수 있습니다(Fielding 외, 2018; Mathers 외, 2016). 선발 절차에는 국가 수준 또는 개별 학교에서 정의한 매우 다양한 도구가 포함될 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 동일한 도구가 다른 방식으로 구현될 수도 있습니다. 이는 서로 다른 도구가 학생 다양성에 차별적인 영향을 미치는지, 그리고 일부 도구가 학생 다양성에 미치는 영향과 관련하여 다른 도구보다 맥락에 더 독립적인지 의문을 제기합니다(Patterson et al., 2016). 본 다중 사이트 연구에서는 다양한 맥락에서 지원자 하위 그룹의 선발 기회와 다양한 선발 도구에 대한 성과를 조사했습니다.
Medical schools and other health professions education (HPE) schools are responsible for selecting qualified students, as well as generating student populations that reflect the diverse society they will serve in the future (General Medical Council, 2015). A diverse healthcare workforce, aside from issues of equity and fairness, is important to improve the cultural competency of healthcare providers, and increase and equalize access to high-quality healthcare for different population groups (Cohen et al., 2002; Morgan et al., 2016). However, student diversity can be affected by the use of selection procedures for undergraduate HPE programs, as selection chances are unequally distributed across subgroups of applicants (Fielding et al., 2018; Mathers et al., 2016). Selection procedures cannot only include a great variety of tools, either defined at a national level or by an individual school, but the same tool can also be implemented in different ways. This raises the question if different tools have differential effects on student diversity (Patterson et al., 2016), and if some tools are more context-independent than others concerning their impact on student diversity. In the present multi-site study, we examined the selection chances of applicant subgroups and their performance on different selection tools in multiple contexts.
지금까지의 연구에 따르면 선발 절차는 주로 사회경제적 지위(SES)가 낮고 소수 민족 출신 지원자의 선발 기회에 부정적인 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났습니다(Fielding 외, 2018; Mathers 외, 2016; Mulder 외, 2022; Stegers-Jager 외, 2015; Steven 외, 2016). 그러나 절차에 사용된 도구의 조합에 따라 하위 그룹 간의 성과 차이가 달라질 수 있기 때문에 이러한 효과가 항상 단순하지는 않을 수 있습니다(Stegers-Jager, 2018). 전통적으로 미국과 유럽의 선발 절차에는 주로 지적 능력을 측정하기 위한 사전 교육 평점 평균(pre-GPA)과 인지 테스트가 포함되었습니다. 지난 수십 년 동안 기존 도구에서 얻은 정보를 추가하고 종종 개인의 자질을 평가하려는 목적으로 광범위한 선발 기준을 포함하는 방향으로 변화해 왔습니다(Niessen & Meijer, 2017; Stegers-Jager, 2018). 이력서(CV)와 상황 판단 테스트(SJT)가 그 예입니다. 이 백서에서는 이러한 구분을 전통적 기준과 확장된 기준이라는 용어로 지칭할 것입니다.
So far, literature has shown that selection procedures mainly negatively affect the selection chances of applicants with lower socio-economic status (SES) and from ethnic minorities (Fielding et al., 2018; Mathers et al., 2016; Mulder et al., 2022; Stegers-Jager et al., 2015; Steven et al., 2016). However, this effect may not always be straightforward, as performance differences between subgroups can depend on the combination of tools used in the procedures (Stegers-Jager, 2018). Traditionally, selection procedures in the United States and Europe mainly included prior education grade point average (pre-GPA) and cognitive tests, aimed at measuring intellectual ability. In the past decades, there has been a shift towards the inclusion of broadened selection criteria, which aim to add to the information derived from traditional tools, and often intend to evaluate personal qualities (Niessen & Meijer, 2017; Stegers-Jager, 2018). Examples include curriculum vitae (CV) and situational judgement tests (SJT). In this paper, we will refer to this distinction with the terms traditional and broadened criteria.
선행 연구에 따르면, 전통적인 기준에서는 높은 사회경제적 지위와 다수인종 지원자에게 유리하게 작용하는 것으로 나타났습니다(Girotti 외, 2020; Juster 외, 2019; Lievens 외, 2016; Stegers-Jager 외, 2015). 학생 다양성에 대한 이러한 부정적 영향을 완화하기 위해 부분적으로 확대된 선발 기준이 도입되었지만, 지금까지의 결과는 일관되지 않습니다(Stegers-Jager, 2018). 예를 들어,
- Lievens 등(2016)은 영국에서 SJT를 도입하면 저소득층 지원자의 대표성은 높아지지만 소수민족 지원자의 대표성은 높아지지 않는다는 사실을 발견했습니다.
- 그러나 미국에서 실시한 유사한 연구에서는 SJT를 추가하는 것이 저소득층과 소수민족 지원자 대표성 모두에 유리한 것으로 나타났습니다(Juster et al., 2019).
Prior research demonstrated performance discrepancies on traditional criteria, favoring higher SES and ethnic majority applicants (Girotti et al. 2020; Juster et al., 2019; Lievens et al., 2016; Stegers-Jager et al., 2015). Although broadened selection criteria were partly introduced to mitigate these adverse effects on student diversity, results so far are inconsistent (Stegers-Jager, 2018). For instance,
- Lievens et al (2016) found that the inclusion of an SJT in the United Kingdom could increase the representation of lower SES applicants, but not of ethnic minority applicants.
- However, a similar study in the United States found that adding an SJT was advantageous for the representation of both lower SES and ethnic minority applicants (Juster et al., 2019).
이는 선발 도구가 다양성에 미치는 영향이 적어도 확대된 기준의 경우 상황에 따라 달라질 수 있음을 시사합니다. 커리큘럼 샘플링 테스트는 국제적인 맥락에서 점점 더 많이 사용되고 있으며 학업 성취도를 예측하는 데 효과적인 것으로 입증된 확장된 기준을 평가하는 또 다른 도구입니다(Niessen et al., 2018). 커리큘럼 샘플링 시험은 학업 프로그램 과목의 대표적인 부분을 모방합니다. 일반적으로 지원자는 입문 과정의 소규모 버전에서 문헌을 공부하거나 동영상 강의를 시청한 후 시험을 치릅니다(Niessen 외, 2018). 커리큘럼 샘플링 시험은 지식, 동기 부여, 학습 시간 등 다양한 속성을 측정하는 데 목적이 있습니다(Niessen & Meijer, 2017). 또한 이러한 테스트는 지원자의 프로그램 '적합성'(예: 시험 및 학습 방식)을 평가하는 데 목적이 있습니다. 저희가 아는 한, 이 특정 도구에 대한 하위 그룹별 성과 차이는 아직 조사되지 않았습니다.
This implies that the effects of selection tools on diversity can be context-dependent, at least in the case of broadened criteria. The curriculum-sampling test is another tool assessing broadened criteria that is increasingly used in international contexts and proved effective in terms of predicting academic achievement (Niessen et al., 2018). Curriculum-sampling tests mimic representative parts of a subject of the academic program. Generally, applicants study literature or watch video lectures from small-scale versions of an introductory course, followed by an exam (Niessen et al., 2018). Curriculum-sampling tests are aimed at measuring a mixture of attributes such as knowledge, motivation, and time spent studying (Niessen & Meijer, 2017). Additionally, these tests intend to assess the applicants’ ‘fit’ with the program (e.g., the way of testing and studying). To our knowledge, subgroup performance differences on this specific tool have not yet been investigated.
국가마다 학생 선발 및 입학에 관한 법률과 규정은 물론 학생 다양성에 관한 고유한 맥락이 있습니다. 네덜란드의 경우, 수년간의 추첨 방식이 사라지고 이제는 프로그램에서 자체적으로 선발 절차를 설계하는 것이 일반적입니다. 프로그램은 자체 개발 및 표준화된 도구 중 어떤 도구를 포함할지, 얼마나 많은 도구를 포함할지(최소 2개 이상)를 독립적으로 결정합니다. 그 결과 매우 다양한 절차와 도구가 등장했습니다. 전국적인 후향적 연구 결과에 따르면 추첨제 폐지 이후 지원자 하위 그룹 간 선발 기회의 불평등이 증가한 것으로 나타났습니다(멀더 외, 2022). 저자들은 여성, 다수민족 지원자, 사회경제적 지위가 높은 지원자가 다른 지원자에 비해 입학 확률이 더 높다는 사실을 발견했습니다. 그러나 이 연구에서는 다양한 선발 절차와 도구의 역할은 고려하지 않았습니다. 이전의 한 단일 사이트 연구에서 이 문제를 밝히려고 시도한 결과, 소수 민족과 낮은 SES 지원자는 학업 기준에서는 낮은 점수를 받았지만 비학업 기준에서는 그렇지 않았다는 결론을 내렸습니다(Stegers-Jager 외., 2015). 연구진은 조사 대상 기관의 경우 남성이 여성에 비해 선발 가능성이 더 높다는 사실을 발견했는데, 이는 다시 학업 기준의 성적과만 관련이 있었습니다. 이는 앞서 언급한 국가적 연구 결과와 모순되는 결과입니다(멀더 외, 2022). 이는 선발이 학생의 다양성에 미치는 영향이 맥락에 따라 달라진다는 가설을 강화합니다. 단일 사이트 연구에서 추가로 관찰된 것은 이민 1세대라는 사실이 더 열악한 선발 결과와 관련이 있다는 점입니다(Stegers-Jager 외., 2015). 이는 국가 코호트 연구에서는 고려되지 않은 변수입니다. 두 연구 모두에 포함되지 않은 잠재적으로 관련성이 있는 마지막 변수는 사전 교육입니다. 최근 보고서에 따르면 외국 교육 경험이 있는 지원자는 '전통적인' 대학 전 과정 지원자에 비해 선발 기회가 더 적었습니다(Van Den Broek et al., 2018).
Every country has its own laws and regulations for selection and admission, as well as a unique context regarding student diversity. Typical for the Netherlands is that, after years of lottery, programs are now responsible for designing their own selection procedures. Programs independently decide which tools they include (both self-developed and standardized), and how many they include (with a minimum of two). This results in a great variety of procedures and tools. Results from a national retrospective study indicate that since the abolishment of lottery, inequality in selection chances between subgroups of applicants has increased (Mulder et al., 2022). The authors found that women, ethnic majority applicants, and applicants with higher SES had a higher probability of admission compared to their peers. However, this study did not take into account the role of the extensive range of possible selection procedures and tools. One previous single-site study attempted to unravel this matter, and concluded that ethnic minority and lower SES applicants had lower scores on academic criteria, but not on non-academic criteria (Stegers-Jager et al., 2015). The researchers discovered that for the institution under consideration, men had higher selection chances compared to women, which was again only related to performance on academic criteria. This contradicts the findings of the aforementioned national study (Mulder et al., 2022). This strengthens the hypothesis that the effects of selection on student diversity are context-dependent. An additional observation of the single-site study was that being a first-generation immigrant was correlated with poorer selection outcomes (Stegers-Jager et al., 2015), a variable that was not accounted for in the national cohort study. A final potentially relevant variable that was included in neither of the studies, is prior education. A recent report indicated that applicants with prior foreign education had smaller selection chances compared to applicants from the ‘traditional’ pre-university track (Van Den Broek et al., 2018).
요컨대, 다양한 선발 도구가 서로 다른 맥락에서 학생의 다양성에 어떤 영향을 미칠 수 있는지는 명확하지 않습니다. 네덜란드의 HPE 프로그램은 선발 절차를 자유롭게 설계할 수 있기 때문에 다양한 선발 도구를 사용하여 여러 절차에서 학생 다양성에 미치는 선발 효과를 비교할 수 있는 독특한 기회를 제공합니다. 본 전향적 다중 사이트 연구는 성별, 이주 배경(인종 지표), 부모 교육(SES 지표), 이전 교육에 따라 지원자 하위 그룹을 대상으로 5개의 학부 HPE 프로그램에 선발될 확률을 평가하는 것을 목표로 했습니다. 또한 두 가지 전통적인 선발 도구(사전 GPA, 생물의학 지식 테스트)와 두 가지 확장된 기준(커리큘럼 샘플링 테스트, 이력서)을 평가하는 도구에 대한 성과 차이를 조사했습니다.
In short, it is not clear how different selection tools can affect student diversity across different contexts. The freedom of Dutch HPE programs to design their selection procedures creates the unique opportunity to compare the effects of selection on student diversity across different procedures with a variety of selection tools. The present prospective multi-site study aimed to evaluate the probability of selection into five undergraduate HPE programs for subgroups of applicants based on gender, migration background (as an indicator of ethnicity), parental education (as an indicator of SES), and prior education. Additionally, we examined performance differences on two traditional selection tools (pre-GPA, biomedical knowledge test), and two tools assessing broadened criteria (curriculum-sampling test, CV).
방법
Method
연구 설계 및 맥락
Design and context
본 연구는 전향적 다중 사이트 코호트 연구에 관한 것입니다. 네덜란드의 5개 대학 수준의 학부 HPE 프로그램에서 데이터를 수집했는데, 여기에는 3개의 의학 프로그램(A, B, C로 표시), 1개의 기술-의료(임상 기술) 프로그램(D로 표시), 1개의 약학 프로그램(E로 표시)이 포함되었습니다. 포함된 프로그램은 네덜란드의 도시와 농촌 등 각기 다른 지역에 위치해 있으며, 모두 학생 선발 과정의 다양성을 높이는 데 중점을 두고 있습니다.
The present research concerns a prospective multi-site cohort study. We collected data from five university-level undergraduate HPE programs in the Netherlands, including three medical programs (labeled A, B, and C), one technical-medical (clinical technology) program (labeled D), and one pharmacy program (labeled E). The included programs were located in different parts of the Netherlands, both in urban and rural areas, and were all concerned about enhancing diversity in their selection processes.
네덜란드의 독특한 점은 다양한 유형의 HPE 학부 프로그램의 입학 요건이 동일하다는 점입니다. 입학 자격을 얻으려면 지원자는 물리, 화학, 생물학 등 수강 과목과 교육 수준에 관한 엄격한 요건을 동일하게 충족해야 합니다. 결과적으로 지원자 풀은 학력 면에서 비교적 동질적이며, 대학 수준의 학부 HPE 프로그램에 지원하는 학생들은 이미 고도로 선택적인 중등 교육으로 인해 학업 능력에 따라 강력하게 사전 선발됩니다(Niessen & Meijer, 2016). 지원자는 자신이 선택한 프로그램에 지원할 때 하나의 특정 교육기관에 지원하게 됩니다. 각 교육기관에는 미리 정해진 정원이 있습니다. 법에 따라 교육기관은 최소 두 가지 이상의 선발 기준을 포함해야 하지만, 앞서 언급했듯이 도구의 내용 및 품질과 같은 추가 요건은 없습니다. 따라서 기관마다 서로 다른 유형의 HPE 프로그램 간에 또는 프로그램 내에서 사용하는 선정 절차에 매우 다양한 차이가 존재합니다. 저희는 두 개 이상의 프로그램에서 사용하는 도구를 연구하여 프로그램 간에 효과가 비슷하거나 다른지 평가했습니다.
Uniquely to the Netherlands is that admission requirements of different types of undergraduate HPE programs are identical. To be eligible, applicants need to meet the same stringent requirements regarding subjects taken (e.g., physics, chemistry, and biology) and educational level. Consequently, the applicant pools are relatively homogeneous in terms of academic background; students who apply to a university-level undergraduate HPE program are already strongly preselected based on academic skills due to highly selective secondary education (Niessen & Meijer, 2016). When applicants apply to their program of choice, they apply to one specific institution. Each institution has a predetermined fixed number of spots. By law, institutions are required to include at least two selection criteria, but as previously mentioned, there are no additional requirements concerning, for instance, the content and quality of the tools. Consequently, great variety exists in the selection procedures that programs employ, both between and within different types of HPE programs at different institutions. We studied tools used by more than one program, to evaluate whether effects were similar or different across programs.
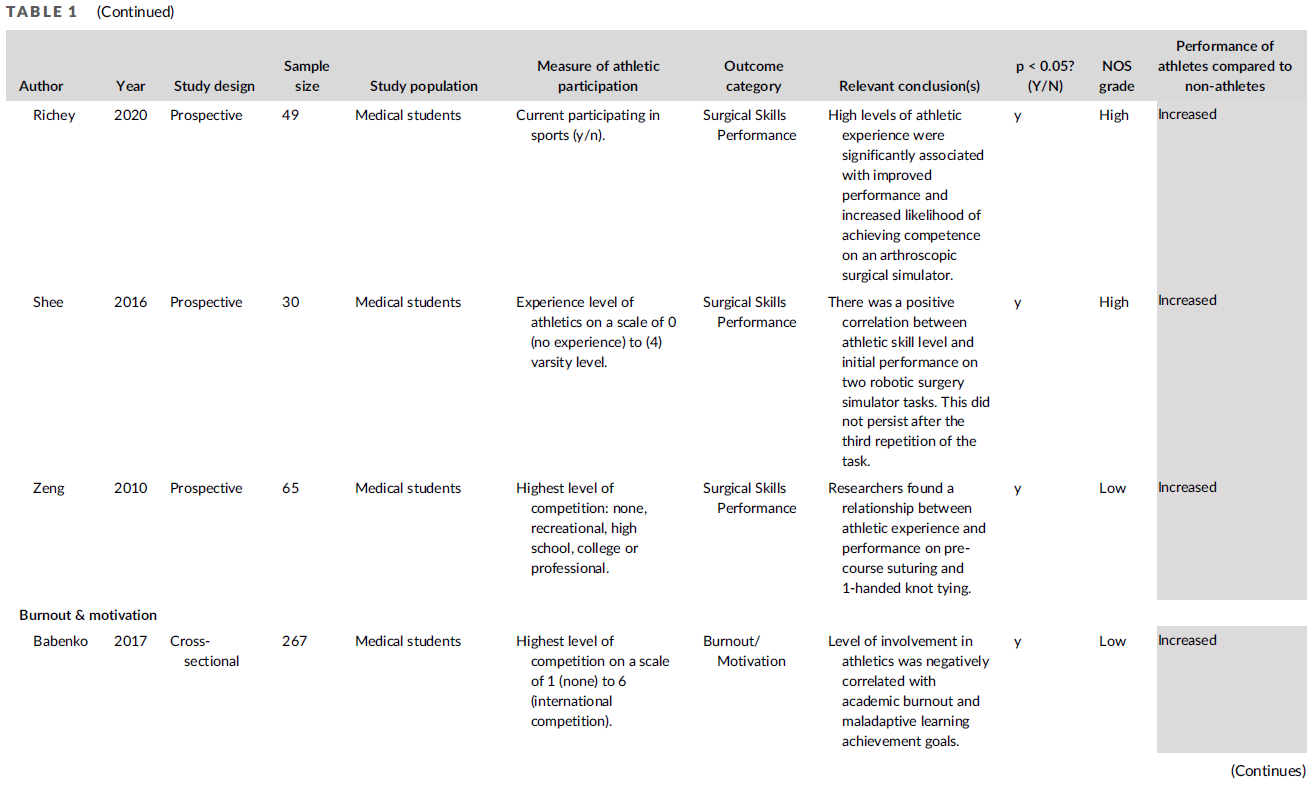
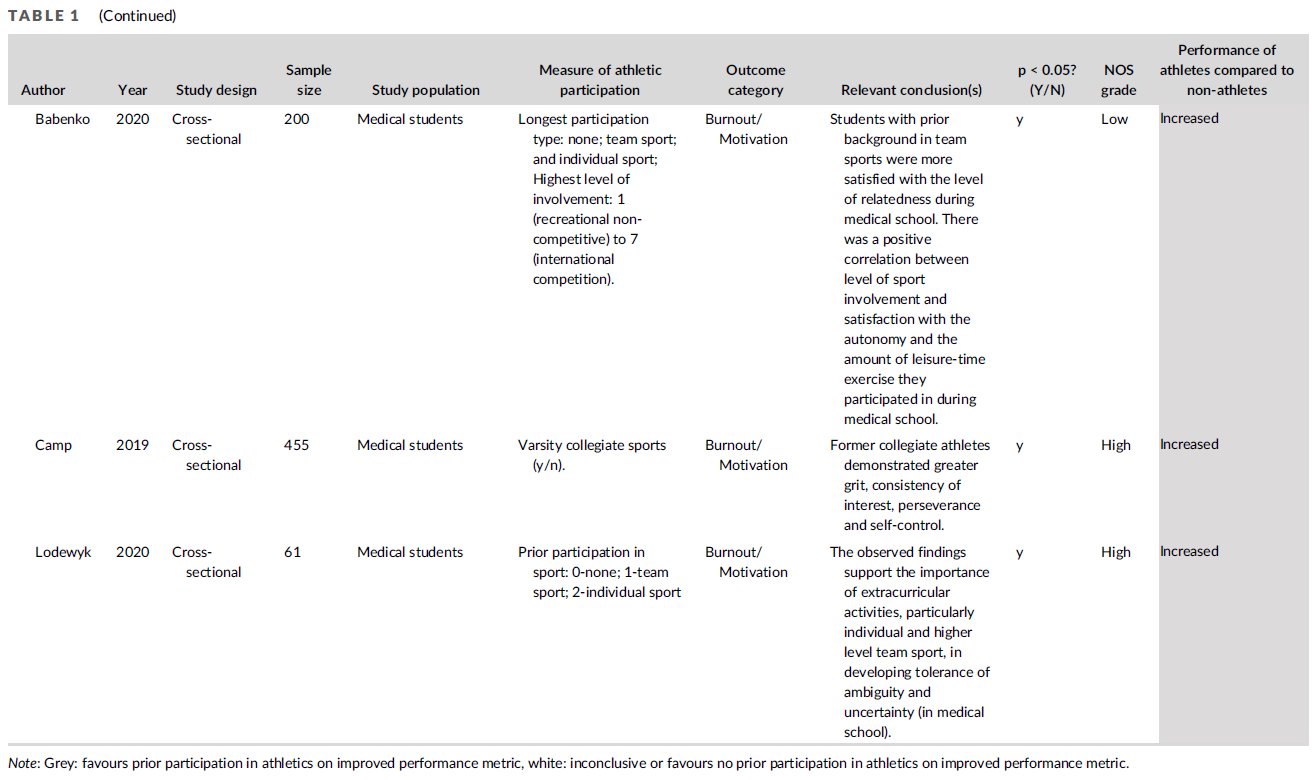
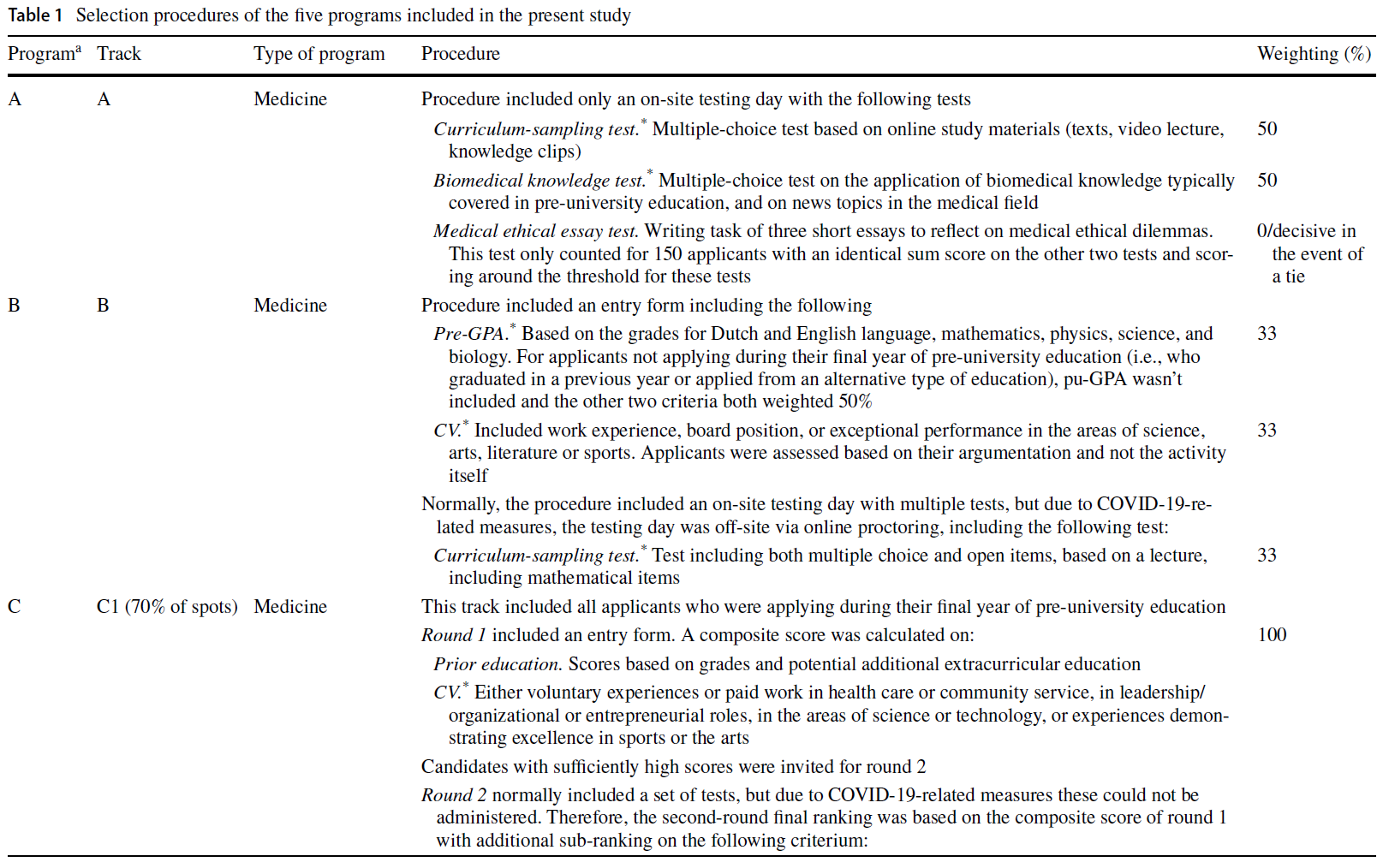
5개 프로그램의 선발 절차는 표 1에 설명되어 있습니다. 여러 프로그램에서 사용한 도구는 사전 GPA, 생물의학 지식 테스트, 커리큘럼 샘플링 테스트, 이력서였습니다.
- 사전 GPA는 일반적으로 수학, 물리, 생물, 화학 등 필수 과목에 대한 지원자의 평균 학교 성적으로 구성되었습니다.
- 생물의학 지식 테스트는 별도의 준비 없이 지원자의 생물의학 과목에 대한 일반적인 지식을 평가했습니다.
- 커리큘럼 샘플링 시험은 대부분 지원자가 시험일 몇 주 전에 받은 강의 및/또는 독서 자료 형태의 준비 자료를 기반으로 진행되었습니다.
- 이력서는 (자발적인) 직업, 인턴십, 특별한 문화 또는 운동 능력에 대한 증거와 같은 과외 활동에 대한 평가로 구성되었습니다.
The selection procedures of the five programs are described in Table 1. The tools used by multiple programs were pre-GPA, biomedical knowledge test, curriculum-sampling test, and CV.
- Pre-GPA comprised of applicants’ average school grades on required subjects, usually mathematics, physics, biology, and/or chemistry.
- Biomedical knowledge tests assessed applicants’ existing general knowledge about biomedical subjects, without requiring any preparation.
- Curriculum-sampling tests were (largely) based on preparatory materials in the form of a lecture and/or reading materials that applicants had received some weeks prior to the testing day.
- CVs consisted of an assessment of extracurricular activities, such as (voluntary) jobs, internships, or evidence of extraordinary cultural or athletic skills.
한 프로그램(D)에서 시행한 바이오메디컬 입학시험(BMAT)의 바이오메디컬 지식 하위 테스트인 표준화된 도구가 포함되었습니다. 샘플에 포함된 다른 모든 선발 도구는 개별 프로그램에서 자체 개발한 것입니다. 따라서 도구의 구체적인 적용은 프로그램마다 달랐으며, 예를 들어 pre-GPA에 포함되는 특정 과목과 시험 문제 유형이 달랐습니다. BMAT를 제외한 모든 선발 도구는 네덜란드어로 시행되었습니다. 프로그램에서 자체적으로 품질 보증을 담당했으며, 저희는 심리측정 정보에 접근할 수 없었습니다.
One standardized tool was included, the biomedical knowledge subtest of the BioMedical Admissions Test (BMAT), which was administered by one program (D). All other selection tools in our sample were self-developed by the individual programs. Consequently, the specific application of the tools differed between the programs, e.g., the specific subjects included in pre-GPA and the types of questions in tests. All selection tools, except for the BMAT, were administered in Dutch. Programs were responsible for their own quality assurance, and we did not have access to psychometric information.

참가자 및 절차
Participants and procedure
2020년 9월에 진행된 선발 절차에 참여한 모든 지원자(N = 3280명)가 참여하도록 초대되었습니다. 프로그램 A, D, E의 경우 현장 테스트 당일에 지원자를 초대했습니다. 프로그램 B와 C는 코로나19 팬데믹 조치로 인해 현장 테스트를 실시하지 않았으며, 선발 과정에서 이메일을 통해 지원자를 모집해야 했습니다.
All applicants engaged in the selection procedures for entry in September 2020 (N = 3280) were invited to participate. For programs A, D, and E, applicants were invited during the on-site testing days. Programs B and C did not perform on-site testing due to COVID-19 pandemic measures, necessitating recruitment via e-mail during the selection procedure.
지원자들은 인구통계학적 설문지를 작성하도록 요청받았습니다. 이 설문조사에서 지원자들은 학번, 성별, 이주 배경, 부모 학력 및 이전 교육에 대해 보고하도록 요청받았습니다. 선발 절차에 대한 성과 데이터는 관련 대학 학생 관리 시스템에서 추출했습니다. 학생 번호는 인구 통계 설문지의 데이터를 성과 데이터와 연결하는 데 사용되었습니다.
Applicants were requested to complete a demographics questionnaire. In this survey, applicants were asked to report their student number, gender, migration background, parental education and prior education. Data on performance on the selection procedures were derived from the related university student administration systems. Student number was used to connect the data from the demographics questionnaire with performance data.
모든 참가자로부터 사전 동의를 얻었습니다. 지원자에게는 참여가 자발적인 것이며 선발 결과에 영향을 미치지 않는다는 사실을 알렸고, 연구진은 선발 위원회와 독립적으로 운영된다는 점을 명시했습니다. 지원자는 연구 참여에 대한 인센티브를 받지 않았습니다. 모든 데이터는 인구통계학적 데이터와 성과 데이터를 결합한 후 즉시 가명 처리되었습니다. 에라스무스 MC의 의료윤리심의위원회는 이 연구가 윤리적 승인 면제 대상임을 선언했습니다.
Informed consent was obtained from all participants. Applicants were informed that participation was voluntary and would not influence their selection outcomes, and we made explicit that the researchers operated independently from the selection committees. Applicants did not receive incentives for participation in the study. All data were pseudonymized immediately after the demographics and performance data were combined. The Medical Ethical Review Committee of Erasmus MC declared the study exempt from ethical approval.
변수
Variables
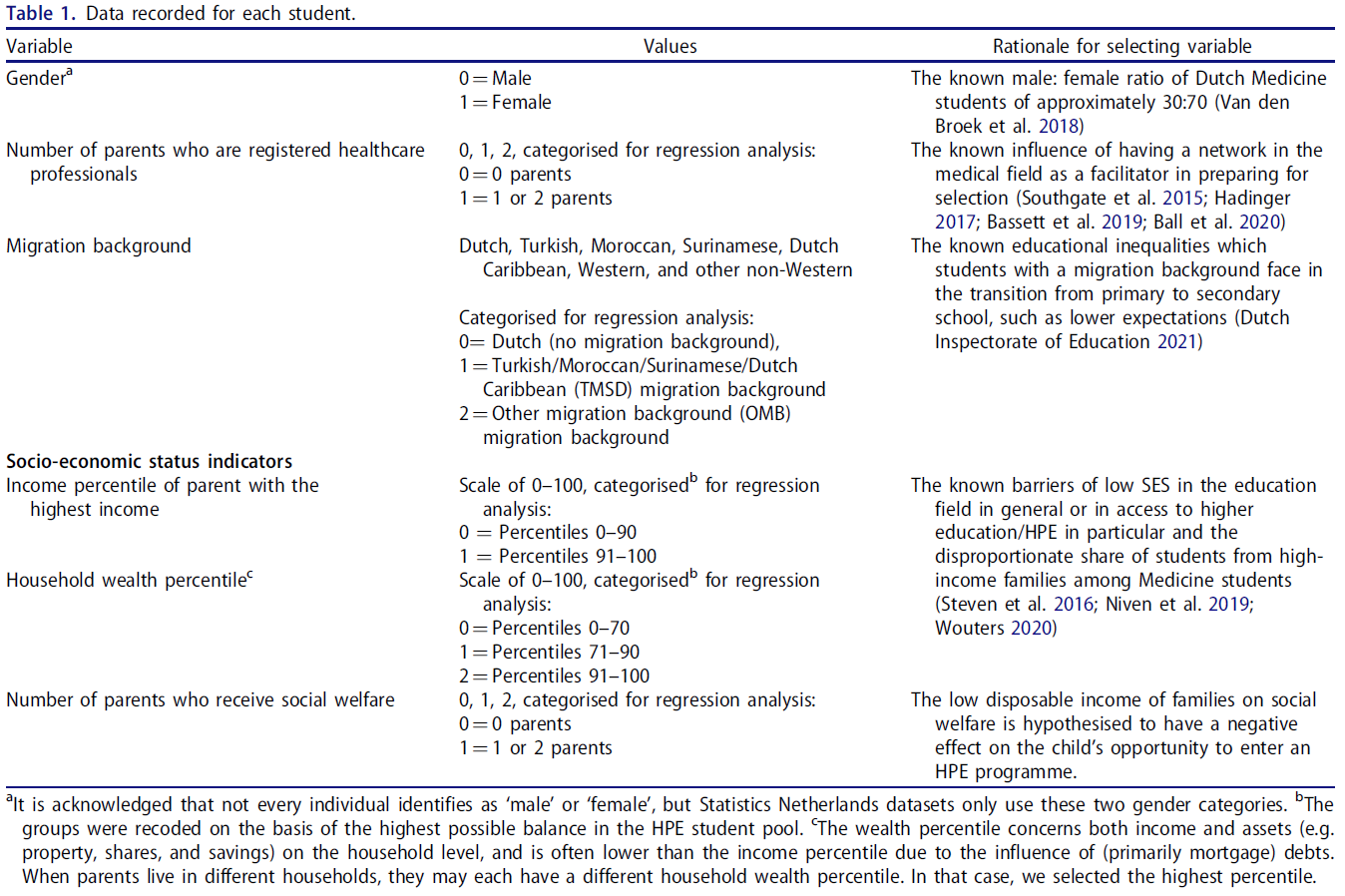
예측 변수에는 성별, 이주 배경, 이전 교육, 부모 교육이 포함되었습니다.
Predictors included gender, migration background, prior education, and parental education.
본 연구에서는 성별의 다양성을 인정하여 지원자가 '남성', '여성', '기타(자유 텍스트 상자)'의 세 가지 범주 중에서 선택할 수 있도록 했습니다.
Gender diversity was acknowledged in the present study, and applicants had the option to choose between three categories: ‘man’, ‘woman’, and ‘other, namely [free text box]’.
이주 배경은 민족의 다차원적 특성을 완전히 포착하지 못한다는 점을 고려하여 민족의 대용어로 사용되었습니다. 이주 배경은 네덜란드 통계청(CBS)에 따라 정의되었습니다. 부모 중 한 명 이상이 네덜란드 밖에서 태어난 경우 개인은 이주 배경을 갖게 됩니다. CBS의 분류법에 따라 서구와 비서구의 이주 배경을 구분했습니다.
- 모든 유럽(터키 제외), 북미, 오세아니아 국가, 인도네시아, 일본을 서구 국가로 간주했습니다.
- 비서양 국가에는 아프리카, 아시아(인도네시아, 일본 제외), 라틴 아메리카, 터키의 모든 국가가 포함되었습니다.
또한 이민 1세대와 이민 2세대를 구분했습니다. 1세대 이민자는 네덜란드 이외의 지역에서 태어났습니다. 네덜란드에서는 이주 배경과 CBS 분류법을 사용하는 것이 민족을 운영하는 표준으로 간주되며, HPE의 연구에서도 마찬가지입니다(예: Mulder 외., 2022; Stegers-Jager 외., 2015).
Migration background was used as a proxy for ethnicity, recognizing that this does not completely capture the multidimensional character of ethnicity. Migration background was defined in alignment with Statistics Netherlands (CBS). Individuals have a migration background when at least one of their parents was born outside of the Netherlands. Based on the taxonomy of CBS, we distinguished between a Western and non-Western migration background.
- All European (excluding Turkey), North American, and Oceanian countries, Indonesia, and Japan were considered Western.
- Non-Western countries included all countries in Africa, Asia (excluding Indonesia and Japan), Latin America, and Turkey.
Additionally, we distinguished between first-generation and second-generation immigrants. First-generation immigrants were born outside the Netherlands. In the Netherlands, the use of migration background and CBS taxonomy are considered the standard for operationalizing ethnicity, also in research in HPE (e.g., Mulder et al., 2022; Stegers-Jager et al., 2015).
네덜란드에서 HPE 프로그램에 입학하는 일반적인 교육 경로는 보건/과학을 전공하는 중등학교의 예비 대학 과정입니다. 그러나 지원자는 다른 형태의 사전 교육을 받은 후에도 HPE 프로그램에 지원할 수 있습니다. 우리는 다음으로 구분했습니다.
- 네덜란드의 표준 대학 예비 교육,
- 대학,
- 고등 직업 교육,
- 모든 형태의 외국 교육,
- 기타 형태의 사전 교육(예: 입시 및 성인 교육)
In the Netherlands, the typical educational route to an HPE program is the pre-university track of secondary school with a health/science profile. However, applicants can apply to HPE programs from alternative forms of prior education. We distinguished between
- standard Dutch pre-university education,
- university,
- higher vocational education,
- all forms of foreign education, and
- other forms of prior education (e.g., entrance exams and adult education).
마지막으로, 부모 교육은 SES를 조작화하기 위해 사용할 수 있는 여러 지표 중 하나에 불과하다는 점을 인정하여 SES의 대리 지표로 사용되었습니다. 부모 교육은 지원자 부모의 교육 수준에 따라 결정되었습니다. 지원자의 부모 중 누구도 고등 교육, 즉 대학 이상의 직업 교육을 받은 적이 없는 경우 지원자를 1세대 대학 지원자로 분류했습니다. 1세대 대학 지원자는 이전 연구에서 의대에 입학할 확률이 낮다는 사실이 입증되었기 때문에 관심 하위 그룹으로 분류되었습니다(Mason 외., 2021; Stegers-Jager 외., 2015). 또한, 이들은 의과대학에 지원할 때 입학 절차에 대한 지식 부족과 재정적 장벽 등 수많은 장애물에 직면합니다(Romero 등, 2020).
Finally, parental education was used as a proxy for SES, acknowledging that this is only one of the many indicators that can be used to operationalize SES. Parental education was determined by the educational level of applicants’ parents. Applicants were categorized as first-generation university applicants when none of their parents had attended higher education, i.e., university or higher vocational education. First-generation university applicants were a subgroup of interest, because previous research has demonstrated that their odds of being selected into medical school are lower (Mason et al., 2021; Stegers-Jager et al., 2015). Additionally, they face numerous obstacles when applying to medical school, including a lack of knowledge about the admission process and financial barriers (Romero et al., 2020).
결과 측정
Outcome measures
다섯 가지 결과 측정이 포함되었습니다. 첫 번째 이분법적 결과 측정은 지원자의 순위 번호에 따라 지원자가 선발되었는지 여부(예/아니오)를 나타냅니다. 나머지 네 가지 결과 측정은 연속적인 것으로 사전 GPA, 커리큘럼 샘플링 테스트, 생물의학 지식 테스트, 이력서의 네 가지 도구에 대한 성과를 반영했습니다. 각 도구에 대해 담당 프로그램은 자체 채점 방식에 따라 원시 점수를 계산했습니다. 그런 다음 각 프로그램은 이 원시 점수를 표준화된 Z 점수로 변환하여 트랙 간 도구 비교를 가능하게 했습니다. 이 Z 점수는 연구진에게 제공되어 분석에 사용되었습니다.
Five outcome measures were included. The first—binary—outcome measure indicated whether an applicant was selected (yes/no), determined by their ranking number. The other four outcome measures were continuous and reflected performance on the four tools: pre-GPA, curriculum-sampling test, biomedical knowledge test, and CV. For each tool, the responsible program calculated a raw score based on its own scoring method. Subsequently, each program transformed these raw scores into standardized Z-scores to enable comparisons of tools between tracks. These Z-scores were made available to the researchers and used for the analyses.
통계 분석
Statistical analyses
다단계 로지스틱 회귀 분석을 수행하여 다양한 예측 변수가 선발 확률에 미치는 영향에 대한 오즈비(OR)를 계산했습니다. OR이 1을 초과하면 선발 가능성이 높아진다는 것을 의미합니다. 프로그램마다 선발 절차의 내용이 다르기 때문에 이 모델에서는 지원자가 지원한 프로그램을 무작위 절편으로 사용했습니다. 프로그램 E는 96%의 높은 선발률로 평균 선발률이 47%인 다른 프로그램과 큰 대조를 이루었기 때문에 분석에서 제외했습니다(부록 1: 표 6). 이 프로그램의 선발률이 이렇게 높았던 이유는 선발 가능 인원에 비해 지원자 수가 적었기 때문입니다.
Multilevel logistic regression analysis was performed to calculate odds ratios (OR) for the effect of the different predictors on the probability of selection. An OR of > 1 indicates an increased likelihood of selection. Since the content of the selection procedure differed between programs, we used the program to which the applicants applied as a random intercept in this model. Program E was excluded from this analysis, given the high selection rate of 96%, which was in large contrast with other programs having an average selection rate of 47% (Appendix 1: Table 6). The selection rate of this program was this high due to the small number of applicants compared to the number of available spots.
다양한 도구의 성능을 비교하기 위해 참여 프로그램에서 제공한 Z 점수를 사용했습니다. 다단계 선형 회귀분석을 수행하여 중복되는 4개의 도구에 대한 Z점수 간의 성능 차이를 평가했습니다. 프로그램 C는 입학정원 제한이 있는 두 개의 독립적인 선택 트랙에 대해 서로 다른 채점 방법을 적용하여(표 1), 두 개의 서로 다른 트랙에 대한 Z점수를 산출했습니다. 따라서 네 가지 도구의 분석을 위해 '프로그램' 대신 '트랙'이라는 변수를 무작위 절편으로 사용했습니다. 앞서 언급했듯이 각 도구의 구체적인 적용이 설정에 따라 다르기 때문에 이러한 무작위 효과를 포함했습니다.
To compare performance on different tools, we used Z-scores that were provided by the participating programs. We performed multilevel linear regression to assess performance differences between Z-scores on the four overlapping tools. Program C applied different scoring methods for two independent selection tracks with intake restriction (Table 1), resulting in Z-scores for the two different tracks. Therefore, we used the variable ‘track’ instead of ‘program’ as a random intercept for the analyses of the four tools. This random effect was included because, as mentioned earlier, the specific application of each tool differed across settings.
'프로그램' 또는 '트랙'을 무작위 절편으로 포함했을 때 절편이 없는 모델에 비해 유의미하게 더 많은 변수를 설명하는지 평가하기 위해 경계 보정을 적용한 확률 비율 테스트를 적용했습니다.
We applied likelihood ratio tests with the boundary correction to assess whether the inclusion of ‘program’ or ‘track’ as a random intercept explained significantly more variance compared to the model without the intercept.
분석은 R 버전 4.0.4의 LME4 1.1.26 및 NLME 3.1.152 패키지를 사용하여 실행되었습니다. 모든 통계 분석에서 가정을 확인했습니다. OR이 1.68 이상 0.60 미만이면 작은 효과, OR이 3.47 이상 0.29 미만이면 중간 효과, OR이 6.71 이상 0.15 미만이면 큰 효과로 해석했습니다(Chen et al., 2010).
Analyses were executed using the LME4 1.1.26 and NLME 3.1.152 packages in R version 4.0.4. For all statistical analyses, assumptions were checked. We interpreted OR of > 1.68 or < 0.60 as a small effect, OR of > 3.47 or < 0.29 as a medium effect, and OR of > 6.71 or < 0.15 as a large effect (Chen et al., 2010).
결과
Results
지원자 특성
Applicant characteristics
총 1935명의 지원자가 연구에 참여했습니다(응답률 59%, 개별 프로그램의 경우 34-81% 범위). 성별은 응답자의 30%가 남성으로 나타났으며, '기타'로 응답한 지원자는 1명이었습니다. 이 지원자는 하위 그룹 분석에서 제외되었기 때문에 결과에는 남성과 여성의 범주만 설명되어 있습니다. 또한 38%는 이주 배경이 있었고, 20%는 다른 형태의 이전 교육을 받은 경험이 있었으며, 25%는 1세대 대학 지원자였습니다. 성별과 연령 측면에서 모든 샘플은 전체 지원자 풀을 대표했습니다. 두 가지 프로그램(C와 E)의 경우, 참여 지원자들이 비참여 지원자들에 비해 선발에서 약간 더 좋은 성적을 거두었습니다(순위 기준).
|In total, 1935 applicants participated in the study (response rate 59%, range 34–81% for individual programs). With respect to gender, 30% of the respondents identified as men, and one applicant identified as ‘other’. This individual was excluded from the subgroup analyses, and therefore only the categories of men and women are described in the results. Furthermore, 38% had a migration background, 20% applied from alternative forms of prior education, and 25% were first-generation university applicants. In terms of gender and age, all samples were representative of the complete applicant pool. For two programs (C and E), participating applicants performed slightly better on the selection (in terms of ranking number) compared to non-participating applicants.
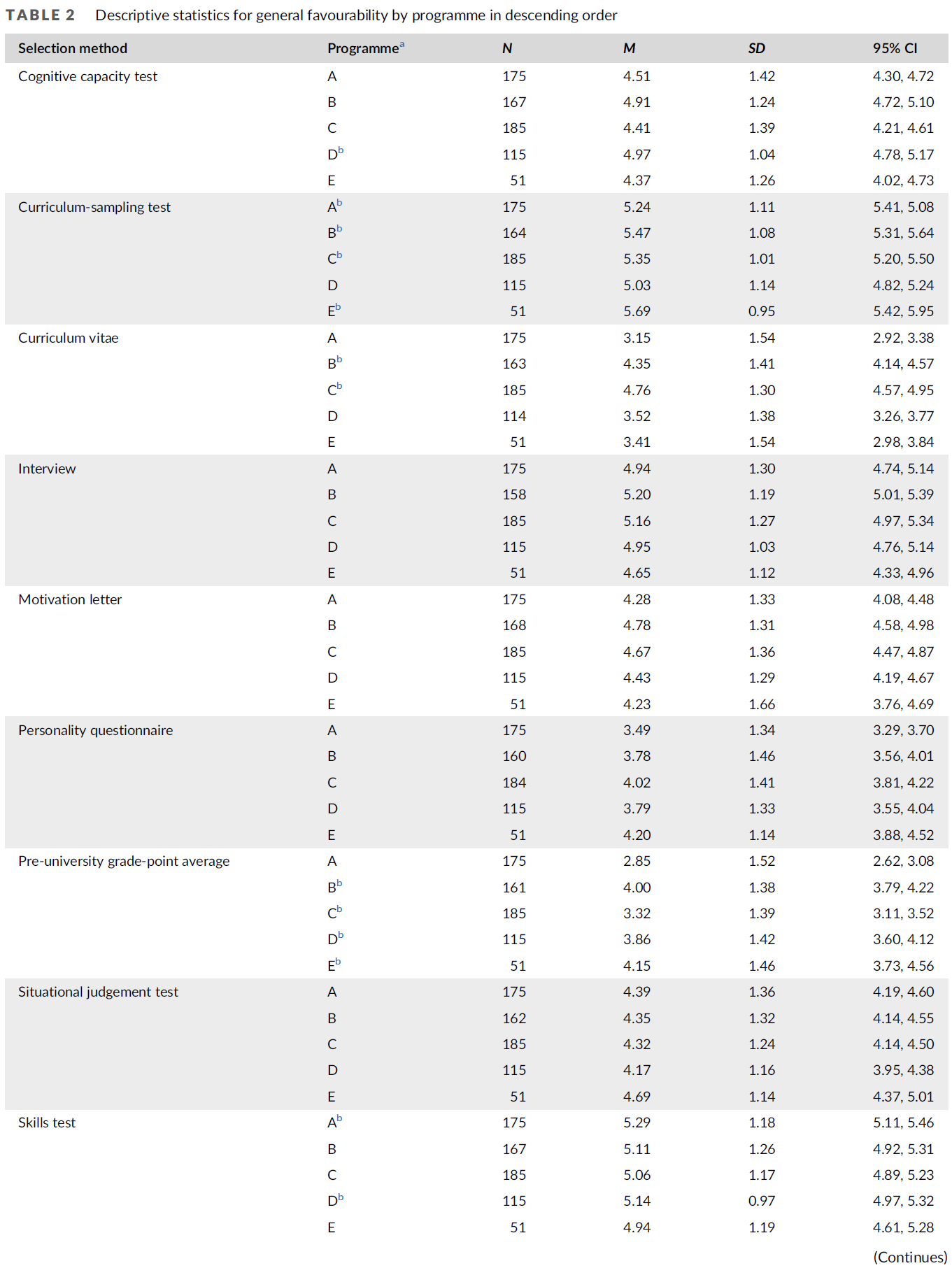
지원자들은 일부 중복되는 도구와 일부 고유한 도구에 노출되었고, 한 프로그램은 선발 확률 분석에서 제외되었기 때문에 지원자 특성 분포는 다단계 분석에서 차이를 보였습니다(표 2). 주목할 만한 점은 생물의학 지식 테스트의 경우 이민 배경을 가진 지원자의 비율이 다른 프로그램에 비해 상대적으로 낮았다는 점입니다(28% 대 36~43%). 또한 사전 학력 평가의 경우, 다른 형태의 사전 교육을 받은 지원자 비율이 상대적으로 적었습니다(10% 대 19~23%). 이는 사전 내신 성적이 지원자 선발 도구에 항상 포함되는 것은 아니기 때문인 것으로 보입니다.
Since applicants were exposed to some overlapping tools, but also to some unique tools, and one program was excluded from the analyses on the probability of selection, the distribution of applicant characteristics differed between the multilevel analyses (Table 2). Noteworthy is that for the biomedical knowledge test, the proportion of applicants with a migration background was relatively low compared to the other programs (28% vs 36–43%). Additionally, for pre-GPA, the proportion of applicants from alternative forms of prior education was comparatively small (10% vs 19–23%). This is probably caused by the fact that pre-GPA is not always included as a selection tool for those applicants.

개별 프로그램마다 관심 있는 지원자의 특성 분포에 차이가 있었습니다(부록 1: 표 6, 7). 가장 눈에 띄는 차이점은 다른 프로그램과 비교했을 때, 표본에서 유일한 지방 프로그램인 프로그램 D는 이민 배경을 가진 지원자(13% 대 32-53%)와 대학 1세대 지원자(15% 대 24-32%)의 비율이 낮았다는 점입니다. 인구통계학적 구성의 차이는 입학 요건의 차이로 인한 것이 아니며, 이는 프로그램 간에 모두 비슷하기 때문입니다. 그러나 위치 및 선발 절차 등 기타 기관 관련 요인으로 인해 특정 프로그램이 특정 하위 그룹에게 더 매력적으로 느껴졌을 가능성이 있습니다(Wouters et al., 2017b).
The individual programs differed in their distribution of the applicant characteristics of interest (Appendix 1: Tables 6, 7). The most notable difference is that compared to the other programs, Program D—the only rural program in the sample—had a lower representation of applicants with a migration background (13% vs 32–53%) and first-generation university applicants (15% vs 24–32%). Differences in demographic composition are not caused by differences in admission requirements, since these were all comparable across programs. However, it is possible that other institutional-related factors made certain programs more attractive to specific subgroups, including location and selection procedure (Wouters et al., 2017b).
선발 확률
Probability of selection
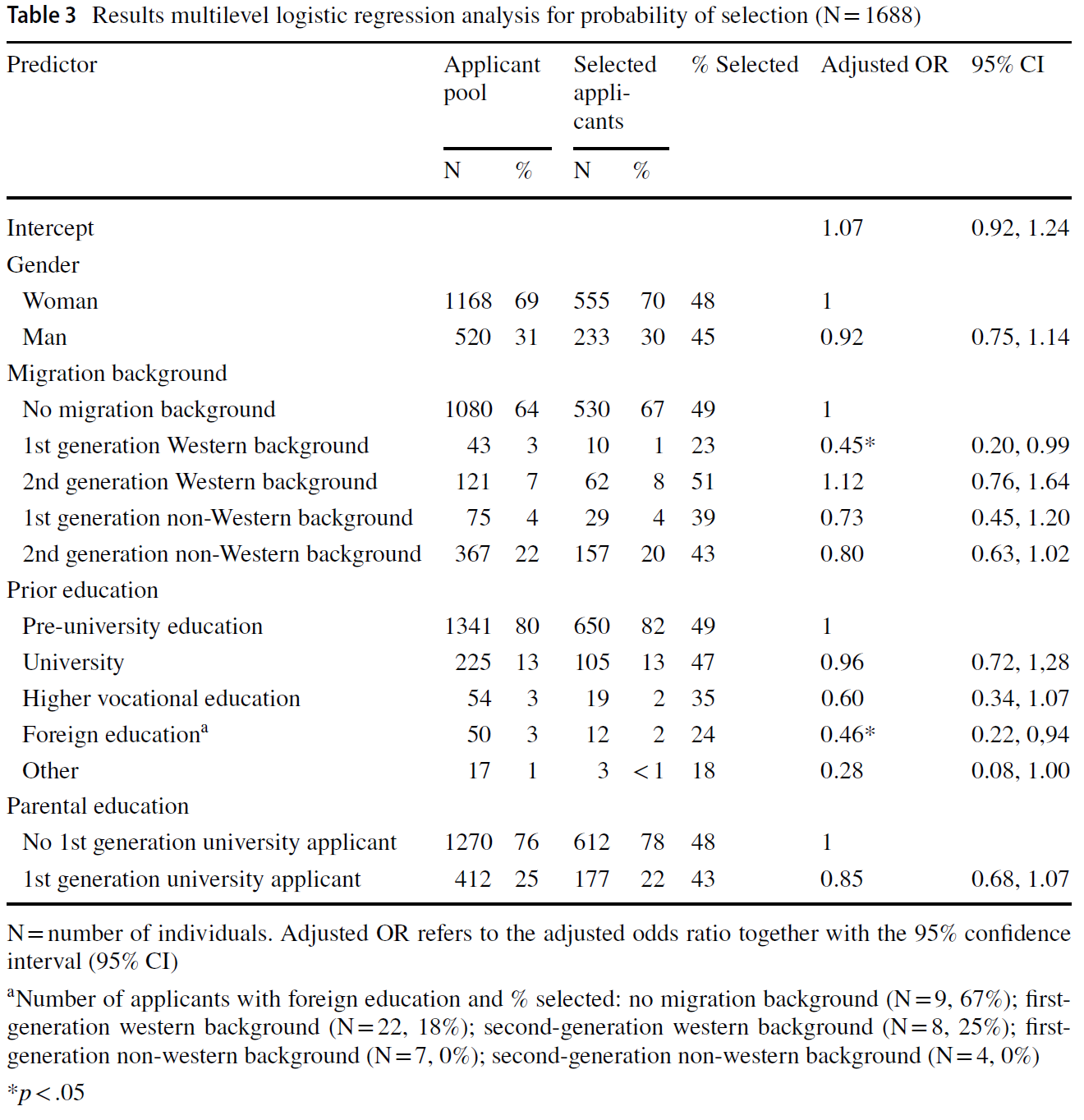
서구 이민 1세대는 이민 배경이 없는 지원자에 비해 선발될 확률이 현저히 낮았으며(23% 대 49%), 조정된 OR은 0.45(95% 신뢰구간[CI] [0.20, 0.99]; 표 3)에 해당합니다. 또한, 외국 교육을 받은 지원자는 표준 대학 전 교육을 받은 지원자보다 선발 확률이 더 낮았습니다(24% vs 49%, 조정된 OR = 0.46, 95% CI [0.22, 0.94]). 둘 다 효과가 작은 것으로 해석할 수 있습니다(즉, OR <0.60). '다른 형태의 사전 교육' 범주는 중간 정도(즉, OR <0.29)이지만 유의하지 않은(수준 0.05) 부정적인 효과(18% 대 49%, 조정된 OR = 0.28, 95% CI [0.08, 1.00])를 보였는데, 이는 이 그룹의 규모가 작았기 때문일 수 있습니다(N = 17). 성별과 부모 교육 정도는 선택 확률과 유의미한 관련이 없었습니다. 프로그램의 무작위 효과는 유의하지 않았으며(SD = 0.00, 95% CI [0.00, 0.21], p = 0.50), 이는 고정된 구조(즉, 성별, 이주 배경, 사전 교육 및 부모 교육 변수)를 고려했을 때 선택 확률의 하위 그룹 차이가 프로그램 간에 유사하다는 것을 나타냅니다.
First-generation Western immigrants were significantly less likely to be selected compared to applicants without a migration background (23% vs 49%), corresponding to an adjusted OR of 0.45 (95% confidence interval [CI] [0.20, 0.99]; Table 3). Additionally, foreign-educated applicants had smaller selection odds than those from standard pre-university education (24% vs 49%, adjusted OR = 0.46, 95% CI [0.22, 0.94]). Both can be interpreted as small effects (i.e., OR < 0.60). The category ‘other forms of prior education’ demonstrated a medium (i.e., OR < 0.29), but non-significant (level 0.05) negative effect (18% vs 49%, adjusted OR = 0.28, 95% CI [0.08, 1.00]), which could be due to the small size of this group (N = 17). Gender and parental education were not significantly associated with the probability of selection. The random effect of program was not significant (SD = 0.00, 95% CI [0.00, 0.21], p = 0.50), indicating that subgroup differences in the probability of selection were similar across programs, given the fixed structure considered (i.e., the variables of gender, migration background, prior education and parental education).
기존 기준에서의 성과
Performance on traditional criteria
Pre-GPA
Pre-GPA
사전 GPA는 4개 프로그램(B, C, D, E)에서 사용되었으며, 이 중 한 프로그램은 두 개의 독립적인 선발 트랙을 사용하여 분석에 다섯 개의 트랙(B, C1, C2, D, E)이 사용되었습니다. 1세대 대학 지원자들은 기존 지원자들에 비해 사전 GPA가 유의미하게 낮았습니다(B = - 0.17, 95% CI [- 0.30, - 0.03]; 표 4, 5). 모든 기준에 대해 Z 점수가 사용되었으므로 표준화되지 않은 B는 SD의 차이를 나타냅니다. 예를 들어, 1세대 대학 지원자의 사전 GPA는 비 1세대 대학 지원자보다 0.17 SD 낮았습니다. 대학 학력 및 '기타 형태의 사전 교육'을 받은 지원자는 일반 대학 1세대 지원자에 비해 사전 GPA가 유의하게 낮았으며(각각 B = - 0.41, 95% CI [- 0.63, - 0.18], B = - 0.76, 95% CI [- 1.42, - 0.11]), 외국 교육을 받은 지원자의 사전 GPA는 유의하게 높았다(B = 1.13, 95% CI [0.54, 1.72]). 성별과 이주 배경은 사전 GPA와 관련이 없었습니다. 트랙의 무작위 효과는 유의하지 않았으며(SD = 0.005, 95% CI [0, 506553], p = 0.50), 이는 고정된 구조를 고려했을 때 사전 GPA에서 발견된 성과 차이가 트랙 간에 유사하다는 것을 나타냅니다.
Pre-GPA was used by four programs (B, C, D, and E), of which one program used two independent selection tracks, resulting in five tracks in the analysis (B, C1, C2, D, and E). Compared to traditional applicants, first-generation university applicants had significantly lower pre-GPAs (B = − 0.17, 95% CI [− 0.30, − 0.03]; Tables 4, 5). As Z-scores were used for all criteria, the unstandardized Bs indicate the difference in SD. Thus, for example, pre-GPAs of first-generation university applicants were 0.17 SD lower than those of non-first-generation university applicants. Applicants with university-level and with ‘other forms of prior education’ had significantly lower pre-GPA (respectively, B = − 0.41, 95% CI [− 0.63, − 0.18]; B = − 0.76, 95% CI [− 1.42, − 0.11] compared to standard pre-university applicants, while pre-GPAs of applicants with foreign education were significantly higher (B = 1.13, 95% CI [0.54, 1.72]). Gender and migration background were not associated with pre-GPA. The random effect of track was not significant (SD = 0.005, 95% CI [0, 506553], p = 0.50), indicating that the performance differences found on pre-GPA were similar across tracks, given the fixed structure considered.


생의학 지식 테스트
Biomedical knowledge test
생의학 지식 테스트는 두 가지 프로그램(A와 D)에서 사용되었습니다. 남성과 대학 수준에서 공부한 지원자는 여성과 표준 대학 이전 교육을 받은 지원자에 비해 생물의학 지식 테스트에서 유의미하게 더 높은 점수를 받았습니다(각각 B = 0.21, 95% CI [0.06, 0.37]; B = 0.32, 95% CI [0.11, 0.52]; 표 6, 7). 이주 배경과 부모 교육은 시험 점수와 관련이 없었으며, 트랙의 무작위 효과는 유의하지 않았습니다(SD = 0.01, 95% CI [0, 12114,82], p = 0.46). 이는 고정된 구조를 고려했을 때 하위 그룹의 성과 차이가 프로그램 간에 유사하다는 것을 나타냅니다.
Biomedical knowledge tests were used by two programs (A and D). Men and applicants who were studying at university-level performed significantly better on biomedical knowledge tests compared to women and applicants from standard pre-university education (respectively, B = 0.21, 95% CI [0.06, 0.37]; B = 0.32, 95% CI [0.11, 0.52]; Tables 6, 7). Migration background and parental education were not associated with test scores, and the random effect of track was not significant (SD = 0.01, 95% CI [0, 12114,82], p = 0.46), indicating that subgroup differences in performance were similar across programs, given the fixed structure considered.
확장된 기준에서의 성과
Performance on broadened criteria
커리큘럼 샘플링 테스트
Curriculum-sampling test
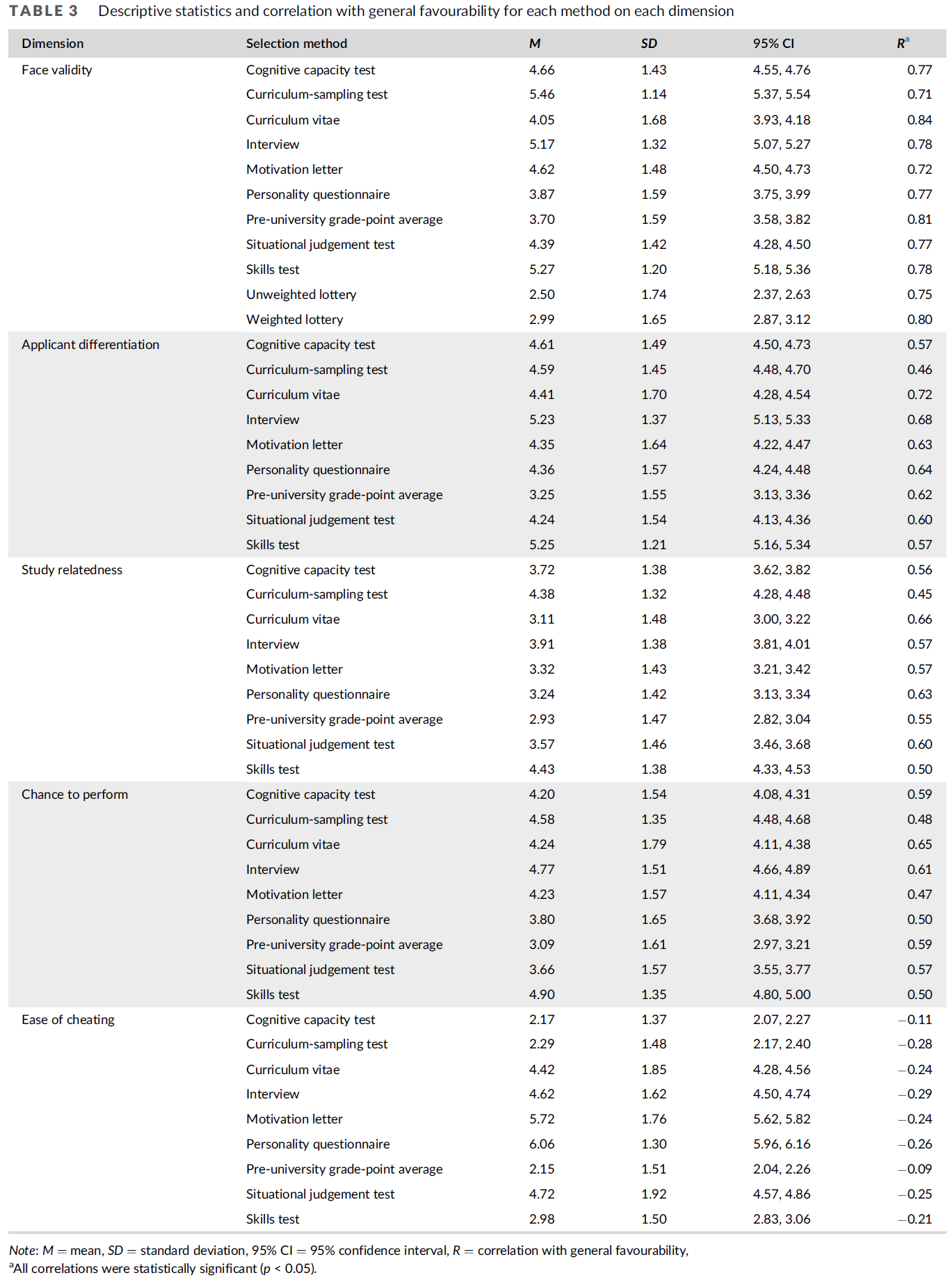
세 가지 프로그램에 커리큘럼 샘플링 테스트(A, B, E)가 포함되었습니다. 비서구권 이주 배경을 가진 지원자(1세대와 2세대 모두)는 기존 지원자에 비해 커리큘럼 샘플링 테스트에서 낮은 점수를 받았습니다(각각 B = - 0.43, 95% CI [- 0.67, - 0.20], B = - 0.21, 95% CI [- 0.34, - 0.10]; 표 6, 7). 이미 대학 수준에서 공부하고 있는 지원자는 일반 예비 대학 지원자에 비해 훨씬 더 우수한 성적을 거둔 반면(B = 0.37, 95% CI [0.21, 0.53]), 외국 교육을 받은 지원자는 시험 점수가 더 낮았습니다(B = - 0.56, 95% CI [- 0.91, - 0.22]). 시험 점수는 성별이나 부모의 학력에 영향을 받지 않았습니다. 고정된 구조를 고려했을 때, 트랙의 무작위 효과는 유의미했습니다(SD = 0.09, 95% CI [0.03, 0.32], p = 0.01). 이는 전반적인 결과가 프로그램마다 다르다는 것을 의미합니다. 커리큘럼 샘플링 테스트를 사용한 개별 프로그램의 설명 통계(부록 1: 표 8)에 따르면 프로그램 E의 경우에만 비 서구권 1세대 배경을 가진 지원자가 이주 배경이 없는 지원자에 비해 평균 Z 점수가 현저히 낮았습니다(M = - 0.86 vs M = 0.29). 이 차이는 프로그램 B의 경우 더 작았고(M = - 0.13 vs M = 0.18), 프로그램 A의 경우 존재하지 않았습니다(M = 0.02 vs M = - 0.01). 주목할 만한 점은 프로그램 E에서 다른 두 프로그램보다 상대적으로 더 많은 지원자가 비서구권 1세대 배경을 가지고 있었다는 점입니다.
Three programs included curriculum-sampling tests (A, B, and E). Applicants with a non-Western migration background, both first-generation and second-generation, scored lower on curriculum-sampling tests compared to their traditional counterparts (respectively, B = − 0.43, 95% CI [− 0.67, − 0.20]; B = − 0.21, 95% CI [− 0.34, − 0.10]; Tables 6, 7). Applicants who were already studying at university-level performed significantly better compared to standard pre-university applicants (B = 0.37, 95% CI [0.21, 0.53]), while applicants with foreign education had lower test scores (B = − 0.56, 95% CI [− 0.91, − 0.22]). Test scores were not influenced by gender or parental education. Given the fixed structure considered, the random effect of track was significant (SD = 0.09, 95% CI [0.03, 0.32], p = 0.01), implying that our overall findings differed between programs. Descriptive statistics of the individual programs employing curriculum-sampling tests (Appendix 1: Table 8) indicate that only for program E, applicants with a first-generation non-Western background had notable low mean Z-scores compared to those without a migration background (M = − 0.86 vs M = 0.29). This difference was smaller for program B (M = − 0.13 vs M = 0.18) and non-existent for program A (M = 0.02 vs M = − 0.01). Noteworthy is that in program E relatively more applicants had a first-generation non-Western background than in the other two programs.
이력서
CV
두 개의 서로 다른 프로그램에서 파생된 세 가지 트랙에는 이력서(B, C1, C2)가 포함되었습니다. 여성 또는 일반 지원자에 비해 남성(B = - 0.17, 95% CI [- 0.31, - 0.02]; 표 6, 7), 서구 이민 1세대(B = - 0.43, 95% CI [- 0.85, - 0.00]), 고등 직업 교육, 외국 교육, '기타 형태의 사전 교육'을 받은 지원자의 CV 점수가 유의하게 낮았습니다(B = - 0.61에서 - 0.81 사이). 부모 교육은 이력서 점수와 관련이 없었습니다. CV에 대한 트랙의 유의미한 효과(SD = 0.25, 95% CI [0.08, 0.76] p <0.001)가 있었으며, 이는 고정된 구조를 고려했을 때 앞서 언급한 효과가 트랙에 따라 다르다는 것을 나타냅니다. 기술 통계(부록 1: 표 9)에 따르면 성별에 따른 성과 격차는 다른 트랙에 비해 트랙 B에서 더 작았습니다(트랙 B: M = 0.04(남성) vs M = 0.17(여성), 트랙 C1: M = - 0.29 vs M = - 0.06, 트랙 C2: M = - 0.11 vs M = 0.25). 전반적으로 서구 이민 1세대가 이민 배경이 없는 지원자보다 점수가 낮았다는 결과는 트랙 B(M = - 0.75 vs M = 0.22)와 트랙 C2(M = - 0.42 vs M = 0.09)에서 나타났지만, 트랙 C1(M = - 0.03 vs M = - 0.14)에서는 나타나지 않았습니다. 이주 배경이 없는 지원자와 비교했을 때, 비 서구권 2세 지원자의 경우 트랙 B(M = - 0.28 vs M = 0.22)에서는 CV 점수가 낮았고, 트랙 C1(M = - 0.17 vs M = - 0.14)에서는 비슷했으며, 트랙 C2(M = 0.45 vs M = 0.09)에서는 CV 점수가 더 높았습니다. 트랙 B의 경우, 다양한 형태의 사전 교육 간에 더 큰 차이가 관찰되었지만, 이는 프로그램 C의 경우 사전 교육에 따라 트랙이 구분되어 트랙 C1에는 표준 대학 전 교육이 집중되고 트랙 C2에는 다른 형태의 사전 교육이 집중된 것과 관련이 있는 것으로 보입니다.
Three tracks derived from two different programs included a CV (B, C1, and C2). Compared to women or traditional applicants, CV scores were significantly lower for men (B = − 0.17, 95% CI [− 0.31, − 0.02]; Tables 6, 7), first-generation Western immigrants (B = − 0.43, 95% CI [− 0.85, − 0.00]), and applicants with higher vocational education, foreign education, and ‘other forms of prior education’ (Bs between − 0.61 and − 0.81). Parental education was not associated with CV scores. There was a significant effect of track for CV (SD = 0.25, 95% CI [0.08, 0.76] p < 0.001), indicating that the aforementioned effects differed across tracks, given the fixed structure considered. Descriptive statistics (Appendix 1: Table 9) suggest that the gender-based performance gap was smaller for track B compared to the other tracks (track B: M = 0.04 (men) vs M = 0.17 (women); track C1: M = − 0.29 vs M = − 0.06, track C2: M = − 0.11 vs M = 0.25). The overall result that first-generation Western immigrants had lower scores than applicants without a migration background was found for track B (M = − 0.75 vs M = 0.22) and track C2 (M = − 0.42 vs M = 0.09), but not for track C1 (M = − 0.03 vs M = − 0.14). Compared to those without a migration background, applicants with a second-generation non-Western background had lower CV scores in track B (M = − 0.28 vs M = 0.22), similar CV scores in track C1 (M = − 0.17 vs M = − 0.14) and higher CV-scores in track C2 (M = 0.45 vs M = 0.09). For track B, larger differences were observed between different forms of prior education, but this is probably related to the fact that for program C, the tracks were distinguished based on prior education, resulting in a large concentration of standard pre-university education in track C1 and a large concentration of other forms of prior education in track C2.
토론
Discussion
학부 HPE 프로그램에서 독특한 선발 절차가 학생 다양성에 미치는 영향을 밝히기 위해서는 성별, 이주 배경(민족성 지표), 부모 교육(SES 지표), 선행 교육에 따른 하위 그룹이 다양한 맥락에서 적용된 선발 도구에서 어떻게 수행되는지에 대한 통찰이 필요합니다. 연구 결과, 전통적이지 않은 배경을 가진 지원자의 선발 확률은 일반적으로 더 낮았지만, 서구 이민 1세대 지원자와 외국 교육을 받은 지원자의 경우에만 유의미한 차이를 보였습니다. 이러한 결과는 프로그램별로 차이가 없었습니다. 그러나 자세히 살펴보면 하위 그룹별 성과에 더 큰 차이가 있고 효과의 가변성이 더 큰 것으로 나타났습니다. 연구 결과, 커리큘럼-샘플링 테스트와 이력서 등 확장된 기준은 SES 관련 성과 차이를 줄일 수 있지만 지원자 인종에 따른 격차는 줄일 수 없다는 결론을 내렸습니다. 또한 하위 그룹별 성과 차이는 확장된 기준에서는 상황에 따라 달라졌지만, 기존 기준에서는 그렇지 않았습니다.
Unraveling the impact of distinctive selection procedures on student diversity in undergraduate HPE programs requires an insight into how subgroups based on gender, migration background (as an indicator of ethnicity), parental education (as an indicator of SES), and prior education perform on the applied selection tools in different contexts. Our results demonstrated that selection chances of applicants with non-traditional backgrounds were generally smaller, but only significantly for applicants with first-generation Western migration backgrounds and applicants with foreign education. These findings did not differ between programs. However, when taking a closer look, we found larger differences in subgroup performance and more variability in effects. We conclude that the broadened criteria under research—curriculum-sampling tests and CVs—may reduce SES-related performance differences, but not disparities based on applicant ethnicity. Furthermore, subgroup performance differences were context-specific for broadened criteria, but not for traditional criteria.
기존 기준 대신 확장된 선발 기준을 적용하면 SES에 따른 성과 격차는 줄일 수 있지만 인종에 따른 성과 격차는 완화하지 못할 수 있다는 첫 번째 주요 결과는 Lievens 등(2016)의 이전 연구를 확인시켜줍니다.
- 연구 대상인 전통적인 기준과 관련하여, 1세대 대학 지원자들은 전통적인 배경을 가진 지원자들에 비해 사전 GPA가 낮다는 사실을 발견했으며, 이는 이전 연구(Griffin & Hu, 2015; Juster 외, 2019; Puddey 외, 2011)에서도 확인되었습니다. 그럼에도 불구하고, 사전 GPA는 다수 민족과 소수 민족 지원자 간에 차이가 없었는데, 이는 소수 민족 그룹 간에 사전 GPA가 매우 다양하기 때문일 수 있습니다(Puddey et al., 2011). 생물의학 지식 테스트에서 SES 기반과 인종 기반에 따른 유의미한 성적 차이는 확인되지 않았습니다. 그러나 이 결과 측정 도구의 표본은 다른 도구에 비해 작고 다양하지 않았으며, 이러한 도구에 대한 국제적인 연구에서도 이러한 차이가 지속적으로 드러나고 있습니다(Girotti 외. 2020; Griffin & Hu, 2015; Juster 외., 2019; Lievens 외., 2016; Puddey 외., 2011).
- 확장된 기준과 관련하여, 본 연구는 다중 기관 환경에서 커리큘럼 샘플링 시험과 이력서에 대한 하위 그룹 성과를 조사한 최초의 연구입니다. 연구 대상인 두 가지 확장된 기준 모두에서 SES에 따른 성과 차이는 발견되지 않았으며, 이는 이전 연구(Griffin & Hu, 2015; Juster 외, 2019; Lievens 외, 2016; Stegers-Jager 외, 2015)와 일치하는 결과입니다. 그럼에도 불구하고, 이전 연구에서는 두 도구 모두에서 이주 배경을 가진 지원자가 불리한 결과를 보인 반면, 본 연구에서는 이주 배경을 가진 지원자가 불리한 결과를 보인 것으로 나타났습니다(Juster et al., 2019; Lievens et al., 2016; Stegers-Jager et al., 2015).
Our first key finding that the implementation of broadened selection criteria instead of traditional criteria potentially reduces performance disparities based on SES, but may not mitigate an ethnicity-related performance gap, confirms the previous work of Lievens et al. (2016).
- With respect to the traditional criteria under research, we found that first-generation university applicants had lower pre-GPAs than applicants from traditional backgrounds, also confirming previous research (Griffin & Hu, 2015; Juster et al., 2019; Puddey et al., 2011). Nevertheless, pre-GPAs did not differ between ethnic majority and ethnic minority applicants, which may be explained by a great variety in pre-GPAs between different ethnic minority groups (Puddey et al., 2011). We did not identify significant SES-based and ethnicity-based performance differences on biomedical knowledge tests. However, the sample for this outcome measure was smaller and less diverse compared to the other tools, and international research on such tools persistently reveals such disparities (Girotti et al. 2020; Griffin & Hu, 2015; Juster et al., 2019; Lievens et al., 2016; Puddey et al., 2011).
- With respect to broadened criteria, our study is the first to investigate subgroup performance on curriculum-sampling tests and CVs in a multi-institutional setting. On both broadened criteria under research, we did not find performance differences based on SES, which resonates with previous research (Griffin & Hu, 2015; Juster et al., 2019; Lievens et al., 2016; Stegers-Jager et al., 2015). Nevertheless, we found that applicants with a migration background were disadvantaged on both tools, whereas previous studies reported mixed findings (Juster et al., 2019; Lievens et al., 2016; Stegers-Jager et al., 2015).
SES에 관한 연구 결과에 대한 한 가지 가능한 설명은 확장된 기준은 표준화되지 않고 프로그램별 특성으로 인해 일반적으로 높은 SES 지원자에게 더 많이 제공되는 코칭을 덜 취약하다는 것입니다(Stemig 외., 2015). 반면에 전통적인 기준은 예를 들어 지원자가 사전 내신 성적을 높이기 위해 개인 과외를 받을 수 있기 때문에 잠재적으로 코칭에 더 취약할 수 있습니다. 동시에 확장된 기준의 표준화가 이루어지지 않으면 문화적 편견의 위험이 증가할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 문화적 편견은 소수 민족 그룹의 구성원이 특정 질문을 다르게 해석할 때 발생할 수 있으며, 이는 이주 배경을 가진 지원자의 낮은 점수를 설명할 수 있습니다(Kim & Zebelina, 2015). 모든 이민 1세대에서 일관되게 효과가 관찰되지 않았기 때문에 언어 편향이 이민 배경에 따른 퍼포먼스 격차에 중요한 역할을 하지는 않았을 것입니다. 또한 이전 연구 결과에 따르면 네덜란드어권 국가 출신 이민자에게도 격차가 존재하는 것으로 나타났습니다(Stegers-Jager 외., 2015).
A possible explanation for our findings regarding SES is that broadened criteria are less prone to coaching—which is generally more available to high SES applicants (Stemig et al., 2015)—due to their unstandardized and program-specific nature. Traditional criteria, on the other hand, are potentially more susceptible to coaching, as applicants can, for instance, purchase private tutoring to increase their pre-GPA. Simultaneously, the lack of standardization of broadened criteria could increase the risk of cultural bias. Cultural bias can, for instance, occur when certain questions are interpreted differently by members from ethnic minority groups, and may explain the lower scores of applicants with migration backgrounds (Kim & Zebelina, 2015). Language bias probably did not play a significant role in performance disparities based on migration background, because effects were not consistently observed amongst all first-generation immigrants. Additionally, results from previous research suggest that disparities also exist for immigrants from Dutch-speaking countries (Stegers-Jager et al., 2015).
두 번째 주요 결과는 확장된 선발 기준의 경우 하위 그룹의 성과 차이가 상황에 따라 달라지는 반면, 기존의 선발 기준은 프로그램 전반에 걸쳐 일관된 효과를 보였다는 것입니다. 이는 두 가지 유형의 기준에 대한 하위집단 성과 차이에 대한 현재 증거에 따른 것으로, 확장된 기준의 사용에 관한 선행 연구 결과는 엇갈리는 반면(Juster 외., 2019; Lievens 외., 2016; Stegers-Jager, 2018; Stegers-Jager et al, 2015), 전통적인 기준의 결과는 소수 민족과 저소득층 지원자에게 불이익을 준다는 점에서 다소 일관성이 있습니다(Griffin & Hu, 2015; Juster 외., 2019; Lievens 외., 2016; Puddey 외., 2011; Stegers-Jager 외., 2015). 또한, 서구 이민 1세대 배경을 가진 남성과 지원자의 이력서 점수가 낮다는 전반적인 결과는 이전의 네덜란드 단일 기관 연구와 일치하지 않았습니다(Stegers-Jager 외., 2015). 이 연구는 겉보기에 비슷해 보이는 도구가 서로 다른 프로그램에서 하위 그룹 성과에 차별적인 영향을 미칠 수 있음을 직접적으로 입증한 최초의 연구입니다. 일반적으로 기준이 넓어지면 더 많은 변수를 허용하고 특정 프로그램 내용에 맞게 조정할 수 있으며, 이는 이러한 도구의 하위 그룹 성과에 대한 상황 의존적 효과가 더 강해지는 원인이 될 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 커리큘럼 샘플링 테스트는 과목, 준비 자료, 준비 시간이 다양합니다. 또한 이전 연구에 따르면 언어의 복잡성(Lievens 외., 2016)과 문제 형식(Edwards & Arthur, 2007)이 시험 성과의 하위집단 차이에 영향을 미칠 수 있다고 합니다. 마찬가지로, 의료 경험은 다양한 배경을 가진 지원자들이 불평등하게 접근할 수 있는 것으로 간주되기 때문에 채점 방법과 이력서 점수에서 고려되는 과외 활동 유형이 중요한 역할을 할 수 있습니다(Wouters, Croiset, Isik 외., 2017).
A second key finding is that for the broadened selection criteria, subgroup performance differences were context-specific, whereas the traditional selection criteria had consistent effects across programs. This is in accordance with the current evidence for subgroup differences in performance on the two types of criteria: results from prior research regarding the use of broadened criteria are mixed (Juster et al., 2019; Lievens et al., 2016; Stegers-Jager, 2018; Stegers-Jager et al., 2015), while the outcomes from traditional criteria are rather consistent in disadvantaging ethnic minority and lower SES applicants (Griffin & Hu, 2015; Juster et al., 2019; Lievens et al., 2016; Puddey et al., 2011; Stegers-Jager et al., 2015). Additionally, the overall finding that men and applicants with a first-generation Western migration background had lower CV scores was not in line with a previous Dutch single-institution study (Stegers-Jager et al., 2015). Our study is the first to directly demonstrate that seemingly comparable tools can have differential effects on subgroup performance across different programs. Typically, broadened criteria allow for more variation and can be further adjusted to the specific program contents, which may be the cause of stronger context-dependent effects on subgroup performance for these tools. For instance, curriculum-sampling tests vary in their subject, preparatory materials, and preparation time. Additionally, previous research suggests that the complexity of the language (Lievens et al., 2016), and question format (Edwards & Arthur, 2007), may contribute to subgroup differences in test performance. Likewise, the scoring method and the type of extracurricular activities that are considered in CV scores may play a role, since healthcare experiences are considered to be unequally accessible to applicants from different backgrounds (Wouters, Croiset, Isik, et al., 2017).
세 번째 주요 결과는 개별 도구에 대한 하위 그룹의 성과 차이가 항상 해당 하위 그룹의 선발 확률에 영향을 미치지는 않는다는 것입니다. 우리는 서구 이민 1세대 배경을 가진 지원자와 외국 교육을 받은 지원자, 즉 이전 연구에서 주목하지 않았던 두 하위 그룹에 대해서만 선발 가능성이 유의미하게 작다는 것을 발견했습니다. 절차 내 및 절차 간 하위집단의 성과에 차이가 있는 도구를 결합하면 전체 효과의 균형이 깨질 수 있으며, 서로 다른 도구의 가중치가 영향을 미쳤을 수 있습니다(Lievens et al., 2016; Stegers-Jager, 2018). 이러한 연구 결과는 네덜란드의 모든 학부 HPE 프로그램 지원자를 대상으로 한 최근의 후향적 연구 결과에 의해 완전히 뒷받침되지는 않습니다(Mulder et al., 2022). 저자들은 통계적 효과 크기 측면에서 무시할 수 있는 수준이었지만 소수 민족, 남성, 사회경제적 지위가 낮은 그룹에서 선발 확률이 유의미하게 낮다는 사실을 발견했습니다(Chen et al., 2010). 본 연구는 일부 프로그램의 전향적 데이터를 사용했으며, 고령 지원자 및 외국 교육을 받은 지원자 등 보다 이질적인 지원자 그룹을 포함했기 때문에 결과 간의 차이는 대상 그룹 간의 차이로 설명할 수 있습니다.
A third key finding is that subgroup differences in performance on individual tools did not always have consequences for the probability of selection of those subgroups. We found that selection chances were only significantly smaller for applicants with a first-generation Western migration background and applicants with foreign education, two subgroups that were left unnoticed by previous research. Combining tools with differential subgroup performance within procedures and across procedures may have counter-balanced the overall effect, and the weightings of different tools may have played a role (Lievens et al., 2016; Stegers-Jager, 2018). Our findings are not fully supported by the results from a recent retrospective study that included applicants to all Dutch undergraduate HPE programs (Mulder et al., 2022). The authors found significantly lower selection probability for additional ethnic minority groups, men and lower SES groups, although the results were negligible in terms of statistical effect size (Chen et al., 2010). The discrepancy between findings may be explained by differences between target groups: the present study used prospective data of a subset of programs and included a more heterogenous group of applicants, including older applicants and those with foreign education.
본 연구의 강점은 여러 프로그램에서 데이터를 수집하고 다단계 분석 접근법을 사용하여 맥락적 차이를 보정하고 조사할 수 있는 기회를 제공했다는 점입니다. 학교가 자체적으로 선발 절차를 설계할 수 있는 네덜란드의 전형적인 입시 시스템 덕분에 다양한 (활용) 도구를 비교할 수 있었습니다. 결과적으로 모든 프로그램에서 모든 도구를 사용하는 것은 아닙니다. 따라서 서로 다른 결과 측정을 직접 비교하거나 서로 다른 도구 간의 성과 상관관계를 조사할 수 없었습니다. 또 다른 한계는 본 연구가 우리가 알기로는 다양한 유형의 학부 HPE 프로그램의 선발 절차를 포함한 최초의 연구이지만, 모든 전공과 기관을 포괄할 수 없었다는 점입니다. 이는 연구 결과의 일반화 가능성에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 또한, 1세대 대학 지원자들이 고등교육으로 전환하는 과정에서 장벽에 직면하는 것으로 나타났기 때문에 부모의 학력을 SES 관련 지표로 포함했지만, 부모의 소득 및 직업과 같이 잠재적으로 관련된 다른 SES 관련 효과를 간과했을 수 있습니다(Girotti 외, 2020; Mulder 외, 2022; Steven 외, 2016). 마찬가지로, 이주 배경은 민족성을 나타내는 안정적이고 객관적인 지표이지만 민족 정체성을 설명하지는 못합니다(Ross et al., 2020; Stronks et al., 2009). 또 다른 한계는 특정 하위 그룹의 경우 표본 크기가 작기 때문에 이러한 결과를 신중하게 해석해야 한다는 것입니다. 마지막으로, 두 가지 선정 절차가 코로나19 조치에 의해 부분적으로 영향을 받아 연구 결과의 일반화 가능성을 떨어뜨릴 수 있습니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 선택 확률의 효과는 해당 분석의 4개 프로그램 간에 큰 차이가 없었으며, 이 중 2개 프로그램이 코로나19의 영향을 받았습니다.
Strengths of our study include that we collected data from multiple programs and that we used a multilevel analytical approach, creating the opportunity to correct for and examine contextual differences. The typical Dutch admissions system, which allows schools to design their own selection procedure, allowed us to compare a variety of (applications of) tools. As a consequence, not all tools were used by all programs. Therefore, direct comparison across different outcome measures and examination of the correlation of performance between different tools were not possible. Another limitation is that although the present study is, to our knowledge, the first to include the selection procedures of a range of different types of undergraduate HPE programs, it was not possible to cover all specialties and institutions. This may have consequences for the generalizability of our findings. Furthermore, we included parental education as a relevant indicator for SES, since first-generation university applicants have been shown to face barriers during the transition into higher education (Stephens et al., 2014), but we may have overlooked other potentially relevant SES-related effects, such as parental income and profession (Girotti et al. 2020; Mulder et al., 2022; Steven et al., 2016). Likewise, migration background is a stable and objective indicator of ethnicity, but does not account for ethnic identity (Ross et al., 2020; Stronks et al., 2009). Another limitation is that for certain subgroups, sample sizes were small, thus those results should be interpreted with caution. Finally, two selection procedures were partly affected by COVID-19 measures, potentially reducing the generalizability of our findings. Nevertheless, the effects of the probability of selection did not differ significantly between the four programs in that analysis, of which two were affected by COVID.
도구 간, 도구 내 하위집단의 차이가 다양하다는 것은 향후 연구에서 도구의 특정 특성이 다양성에 미치는 영향을 조절하는 역할을 할 수 있는지 여부를 결정해야 함을 의미합니다. 이를 통해 모범 사례를 파악할 수 있습니다. 또한, 이번 연구 결과만으로는 도구의 다양한 가중치가 미치는 영향에 대한 결론을 도출할 수 없습니다. 따라서 우리는 도구의 다양한 가중치가 학생의 다양성에 미치는 영향을 조사하자는 이전 제안을 지지합니다(Stegers-Jager, 2018). 향후 연구에서는 선발 도구가 하위 그룹별로 학업 성취도를 다르게 예측하는지 여부를 조사하여 우리가 발견한 성취도 격차가 편향성(특정 하위 그룹에 대한 과소 예측 또는 과대 예측)과 일치하는지 여부를 확인해야 합니다. 마지막으로, 향후 연구에서는 HPE 선발의 맥락에서 비전통적 배경을 가진 지원자 하위 그룹의 구체적인 기본 특성과 요구 사항을 파악하여 선발 과정과 선발 후에도 더 나은 지원을 제공할 수 있도록 해야 합니다(Lievens, 2015; Wouters, 2020). 예를 들어, 다른 형태의 사전 교육을 받은 지원자는 이전 교육 경험과 크게 다를 수 있는 HPE 선발에서 기대하는 바를 관리하는 데 어려움을 겪을 수 있습니다(Katartzi & Hayward, 2020; Rienties & Tempelaar, 2013).
The variety in subgroup differences between and within tools implies that future research should determine whether specific characteristics of tools can play a moderating role in their effects on diversity. This could lead to the identification of best practices. Furthermore, based on our results we cannot draw conclusions with respect to the effect of different weightings of tools. Therefore, we endorse a previous suggestion to investigate the effects of different weightings of tools on student diversity (Stegers-Jager, 2018). Future studies should also examine whether selection tools differentially predict academic performance for different subgroups, to determine whether the performance disparities we found correspond with bias (i.e., underprediction or overprediction for certain subgroups). Finally, future research should identify the specific underlying characteristics and needs of subgroups of applicants with non-traditional backgrounds within the context of HPE selection, to provide better support during and, as suggested by others (Lievens, 2015; Wouters, 2020), also after selection. For instance, applicants from alternative forms of prior education may face difficulties managing the expectations in HPE selection that can strongly differ from their previous educational experiences (Katartzi & Hayward, 2020; Rienties & Tempelaar, 2013).
실용적인 관점에서 볼 때, 하위 그룹 간 성과 차이의 맥락별 특이성은 HPE 프로그램이 다른 맥락의 기존 연구에만 의존하지 않고 선발 절차가 학생 다양성에 미칠 수 있는 영향에 대한 지속적인 평가를 수립해야 한다는 것을 나타냅니다. 또한, 당사는 프로그램이 상황에 따라 효과가 달라질 수 있다는 점을 염두에 두고 SJT(Juster et al., 2019) 및 다중 미니 인터뷰(Griffin & Hu, 2015)와 같이 부정적인 영향을 줄이고 필요한 다양성을 명시적으로 증진할 수 있는 대체 도구를 양심적으로 포함하거나 개발할 것을 권장합니다. 학교별 선발 절차가 교육과정과 일치하는 선발 절차는 높은 예측 가치를 가질 수 있기 때문에 학교별 선발 절차를 적용하고자 하는 욕구를 인정합니다(Schreurs et al., 2020). 동시에, 이는 프로그램이 부정적인 영향을 포함하여 선발 절차의 타당성에 대한 다양한 측면을 평가할 책임이 있음을 의미합니다(Schreurs, 2020). 또한 프로그램은 다양한 규범화 그룹을 통해 도구를 검증하는 것도 고려할 수 있습니다(Padilla & Borsato, 2008).
From a practical viewpoint, the context-specificity of subgroup differences in performance indicates that HPE programs need to establish continuous evaluation of the possible effects of their selection procedures on student diversity, rather than only relying on existing research in other contexts. Additionally, we encourage programs to conscientiously include and/or develop alternative tools that can reduce adverse impact and explicitly promote well-needed diversity, such as SJTs (Juster et al., 2019) and multiple mini-interviews (Griffin & Hu, 2015), while keeping in mind that effects can be context-specific. We acknowledge the desire to apply school-specific selection procedures, as selection procedures that align their contents with the curriculum can have high predictive value (Schreurs et al., 2020). Simultaneously, this creates a responsibility for programs to evaluate different aspects of the validity of their selection procedure, including adverse impact (Schreurs, 2020). Additionally, programs could consider validating their tools with diverse norming groups (Padilla & Borsato, 2008).
결론적으로, 학부 HPE 프로그램 선발은 의도치 않게 학생의 다양성에 영향을 미쳐 공평한 입학을 저해할 수 있습니다. 기존 기준에 비해 확장된 기준은 SES 관련 성과 차이를 줄일 수 있지만 인종에 따른 격차는 줄일 수 없습니다. 확장된 기준의 경우, 하위 그룹의 성과 차이도 상황에 따라 달라집니다. 따라서 우리는 다양성에 대한 선발의 지속적인 평가 효과, 기존 도구 내에서 모범 사례의 식별, 학생 다양성에 긍정적이거나 중립적인 영향을 미치는 도구의 포함, 충분한 품질 관리가 필요하다고 촉구합니다.
In conclusion, selection into undergraduate HPE programs can unintentionally impact student diversity, hindering equitable admission. Compared to traditional criteria, broadened criteria can reduce SES-related performance differences, but not disparities based on ethnicity. For broadened criteria, subgroup differences in performance also vary across contexts. We, therefore, call for continuous evaluation effects of selection on diversity, the identification of best practices within existing tools, the inclusion of tools with a positive or neutral impact on student diversity, and sufficient quality control.
Selection tools and student diversity in health professions education: a multi-site study
PMID: 36653557
PMCID: PMC9848043
DOI: 10.1007/s10459-022-10204-9
Free PMC article
Abstract
Student diversity in health professions education (HPE) can be affected by selection procedures. Little is known about how different selection tools impact student diversity across programs using different combinations of traditional and broadened selection criteria. The present multi-site study examined the chances in selection of subgroups of applicants to HPE undergraduate programs with distinctive selection procedures, and their performance on corresponding selection tools. Probability of selection of subgroups (based on gender, migration background, prior education, parental education) of applicants (N = 1935) to five selection procedures of corresponding Dutch HPE undergraduate programs was estimated using multilevel logistic regression. Multilevel linear regression was used to analyze performance on four tools: prior-education grade point average (pe-GPA), biomedical knowledge test, curriculum-sampling test, and curriculum vitae (CV). First-generation Western immigrants and applicants with a foreign education background were significantly less likely to be selected than applicants without a migration background and with pre-university education. These effects did not vary across programs. More variability in effects was found between different selection tools. Compared to women, men performed significantly poorer on CVs, while they had higher scores on biomedical knowledge tests. Applicants with a non-Western migration background scored lower on curriculum-sampling tests. First-generation Western immigrants had lower CV-scores. First-generation university applicants had significantly lower pe-GPAs. There was a variety in effects for applicants with different alternative forms of prior education. For curriculum-sampling tests and CVs, effects varied across programs. Our findings highlight the need for continuous evaluation, identifying best practices within existing tools, and applying alternative tools.
Keywords: Admission; Adverse impact; Selection; Student diversity; Undergraduate education.
© 2023. The Author(s).