CanMEDS 2025의 적응적 전문성(Can Med Educ J. 2023)
Adaptive Expertise in CanMEDS 2025

소개
Introduction
적응형 전문성은 급변하는 세계에서 효과적이고 혁신적으로 진료하고 학습하는 데 필요한 지식과 기술의 진화, 개선 및 개발과 관련된 역량을 통합합니다. 이 개념은 최근의 문헌 검토에서 CanMEDS 의사 역량 프레임워크에서 잘 드러나지 않는 필수 개념으로 확인되었습니다.1 이 원고는 이 개념과 이전 및 향후 CanMEDS의 반복에 대한 연관성을 요약하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
Adaptive expertise incorporates competencies related to the evolution, refinement, and development of the knowledge and skills required to practice and learn effectively and innovatively in a rapidly changing world. It was identified as an essential concept that was underrepresented in the CanMEDS physician competency framework in a recent literature review.1 This manuscript aims to summarize the concept and its links to former and future iterations of CanMEDS.
적응형 전문성이란 무엇이며 의사 역량에 중요한 이유는 무엇인가요?
What is adaptive expertise and why is it important to physician competency?
적응적 전문성은 잘 알려진 문제에 직면했을 때 이전 지식을 효율적이고 효과적으로 적용하는 것과 이전 지식이 불충분할 때 새로운 지식을 창출하여 해결책을 마련하는 것 사이의 균형을 강조하는 전문가 개발 및 성과 모델입니다. 이와는 대조적으로 일상적 전문성은 적응적 전문성의 효율성 차원만을 반영하는 것으로 이해됩니다. 적응적 전문성의 '효율성'과 '혁신' 사이의 균형은 일상적인 문제 해결을 학습과 개선의 기회로 인식하는 접근법으로 보완됩니다.2,3 따라서 이전 지식의 적용이 불충분한 문제에 직면했을 때
- 적응적 전문성은 지식을 유연하게 사용하고 새로운 솔루션을 생성하는 능력을 가능하게 하는 반면,
- 일상적 전문성은 '알려진 솔루션에 미지의 문제를 맞추려는 시도'를 하다가 실패로 이끌게 됩니다."4
Adaptive expertise is a model of expert development and performance that emphasizes a balance between the efficient and effective application of previous knowledge when facing well-known problems and the creation of new knowledge to generate solutions when previous knowledge is insufficient. In contrast, routine expertise is understood to reflect only the efficiency dimension of adaptive expertise. This balance between ‘efficiency’ and ‘innovation’ in adaptive expertise is complemented by an approach to practice that recognizes daily problem solving as an opportunity to learn and improve.2,3 Thus, when facing problems for which the application of previous knowledge is insufficient,
- adaptive expertise enables the flexible use of knowledge and the ability to generate new solutions while
- routine expertise will result in failed attempts to ‘fit unknown problems to known solutions.’4
적응적 전문성은 무엇을 해야 하는지(절차적 유창성)와 왜 해야 하는지(개념적 이해)를 모두 아는 것이 특징입니다.5 이러한 개념적 이해는 새롭고 불확실한 임상 상황의 가변성에 적응할 수 있게 합니다. 즉, 알려진 해결책이 충분하지 않은 경우 적응적 전문가는 근본적인 '이유'를 다루는 새로운 해결책을 생성할 수 있습니다. 적응형 전문성을 키우려면 교육이 효과적인 지식 보유와 적용에만 중점을 두는 것에서 벗어나 학생들이 새로운 지식을 지속적으로 학습하고 생성할 수 있도록 준비시키는 방향으로 전환되어야 합니다. 이러한 역량을 '미래 학습을 위한 준비(PFL)'로 정의할 수 있습니다.6
Adaptive expertise is characterized by both knowing what to do (procedural fluency) as well as knowing why you’re doing it (conceptual understanding).5 It is this conceptual understanding that permits adaptation to variability in novel and uncertain clinical situations i.e. if known solutions are insufficient, adaptive experts can generate new solutions that still address the underlying ‘why’. To foster the development of adaptive expertise, education must shift beyond a sole emphasis on effective knowledge retention and application towards preparing students to continue to learn and generate new knowledge. This capacity has been defined as ‘preparation for future learning (PFL).6
보건 전문직 교육에서 PFL을 지원하는 교육적 접근법에는 다음이 포함됩니다.7,8
- a) 임상 징후 및 증상을 근본적인 메커니즘과 명시적으로 통합(예: "왜"라고 묻거나 말하기),
- b) 학생들에게 의미 있는 변형에 노출(예: "만약에 이렇다면.." 질문하기),
- c) 학습에서 투쟁과 발견을 활용한 다음, 즉각적인 피드백과 통합이 뒤따르는 것
불가피하게 보건 전문가는 정식 교육을 받지 않은 질환을 가진 환자를 마주하게 될 것입니다. 따라서 새로운 문제에 직면하여 새로운 지식을 창출하고 학습하는 능력은 의사가 환자의 고유한 요구에 대응하고 끊임없이 변화하는 역동적인 의료 종사자 간 네트워크 내에서 치료를 제공할 수 있도록 보장합니다.9
In health professions education, pedagogical approaches that support PFL include
- a) explicit integration of clinical signs and symptoms with underlying mechanisms (e.g asking or telling “why”),
- b) exposing students to meaningful variation (e.g asking “what if” questions) and
- c) leveraging struggle and discovery in learning followed by immediate feedback and consolidation.7,8
Inevitably, health professionals will face patients presenting with conditions for which they have not received formal training. Thus, the ability to create new knowledge and learn in the face of novel problems ensures that physicians are responsive to the unique needs of their patients, as well as able to provide care within ever-changing, dynamic, interprofessional networks of healthcare workers.9
적응형 전문성은 2015 CanMEDS 역량 프레임워크에서 어떻게 표현되나요?
How is adaptive expertise represented in the 2015 CanMEDS competency framework?
의료 전문가 역할은 환자 중심의 임상 평가 및 관리, 임상 의사결정의 복잡성, 모호성, 불확실성, 의사결정 시 진화하는 지식의 활용 등 적응적 전문성의 여러 측면을 반영합니다. 그러나 2015년 프레임워크에는 이러한 역할과 관련하여 적응적 전문성에 대한 구체적인 언급이 부족하여(표 1A 및 및1B),1B) 교육자가 효과적이고 혁신적으로 실습하고 학습하는 데 필요한 지식과 기술을 의도적으로 배양할 수 있는 환경이 조성되지 않을 수 있습니다. 적응형 전문지식을 CanMEDS의 핵심 의료 전문가 역량으로 명시적으로 통합하면 의료 전문지식과의 관계를 강조하고, 일상적인 진료에서 7가지 CanMEDS 역할을 모두 통합하는 데 핵심적인 기능을 강조하며, 전문 역량 및 지속적인 전문성 개발의 지표로서 진료에서 새로운 지식을 혁신하고 창출하는 역량을 장려할 수 있습니다.
The Medical Expert role reflects many aspects of adaptive expertise: patient-centered clinical assessment and management; complexity, ambiguity, and uncertainty in clinical decision-making; and drawing on an evolving body of knowledge when making decisions. However, the 2015 framework lacks specific reference to adaptive expertise in relation to this role (Table 1A and and1B),1B), which may create an environment where educators are not primed to deliberately cultivate the necessary knowledge and skills required to practice and learn effectively and innovatively. Explicitly incorporating adaptive expertise as a key Medical Expert competency in CanMEDS would highlight its relationship with medical expertise, underscore its central function to the integration of all seven CanMEDS roles in daily practice, and promote the capacity to innovate and create new knowledge in practice as a marker of professional competence and continuing professional development.
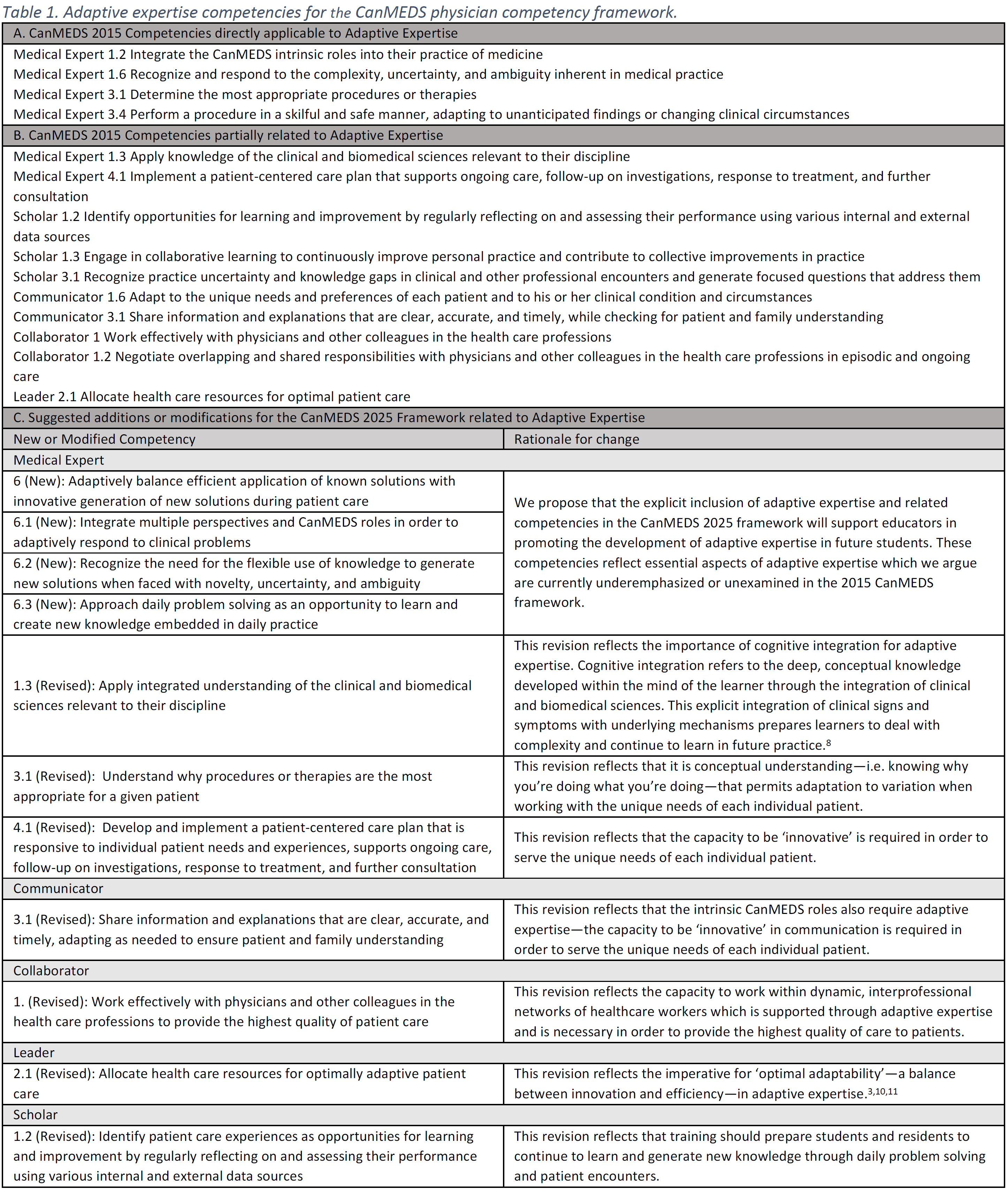
2025년 CanMEDS 역량 프레임워크 내에서 적응형 전문성을 어떻게 더 잘 표현할 수 있을까요?
How can adaptive expertise be better represented within the 2025 CanMEDS competency framework?
임상 의사 결정에서 적응형 전문 지식의 중요성을 인식하여 의료 전문가 역할에 새로운 핵심 역량을 통합할 것을 제안합니다(표 1C). 이 역량에는 효율성과 혁신 사이의 균형을 맞추고, 다양한 관점을 수용하며, 임상 진료 전반에 걸쳐 학습할 수 있는 역량이 포함됩니다. 적응형 전문성을 의료 전문가 역할의 핵심 역량으로 설정함으로써, 우리는 CanMEDS 프레임워크에서 의료 전문성의 중심적인 역할과 내재적인 역할을 자신의 업무 범위에 통합하는 방법을 인식하고 있습니다. 또한 커뮤니케이터, 협력자, 리더, 학자 역할에 속하는 역량들이 이러한 영역에서 적응형 전문성의 중요한 요소를 더 잘 통합할 수 있도록 약간의 제안을 했습니다(표 1C). 발달적 관점에서 볼 때, 분야별 교육에 적응적 전문성을 조기에 도입하는 것은 PFL을 포함하는 교육이 지속적인 전문성 개발에서 임상적 의사 결정의 지속적인 역량과 성장을 보장하는 데 도움이 될 수 있음을 인식하는 것입니다. 초심자에서 숙련자로 넘어가는 CanMEDS 마일스톤의 구성은 적응형 전문성과 더욱 연계되어 전문적 역량의 지표로서 실무에서 새로운 지식을 혁신하고 창조하는 역량을 촉진할 수 있습니다.
Recognizing the importance of adaptive expertise in clinical decision-making, we propose incorporating a new key competency into the Medical Expert role (Table 1C). Its enabling competencies incorporate the capacity to balance between efficiency and innovation, to embrace multiple perspectives, and to learn throughout clinical practice. By situating adaptive expertise as a key competency within the Medical Expert role, we recognize the central role of medical expertise in the CanMEDS framework and how it incorporates the intrinsic roles into one’s scope of practice. Additionally, we have made minor suggestions to enabling competencies under the Communicator, Collaborator, Leader, and Scholar roles to better integrate important elements of adaptive expertise in these areas (Table 1C). From a developmental perspective, the introduction of adaptive expertise early within discipline-specific training recognizes that education that includes PFL can help ensure that sustained competence and growth in clinical decision-making is accounted for in continuing professional development. The progression from novice to mastery in the organization of CanMEDS milestones can further align with adaptive expertise to promote the capacity to innovate and create new knowledge in practice as a marker of professional competence.
Adaptive Expertise in CanMEDS 2025
PMID: 36998497
PMCID: PMC10042796
DOI: 10.36834/cmej.75445
'Articles (Medical Education) > 교육과정 개발&평가' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 구조적 역량: 낙인과 불평등에 관한 새로운 의학적 관여의 이론화(Soc Sci Med. 2014) (0) | 2024.01.26 |
|---|---|
| CanMEDS 2025의 지구보건(Can Med Educ J. 2023) (0) | 2024.01.20 |
| CanMEDS 2025의 임상추론(Can Med Educ J. 2023) (0) | 2024.01.20 |
| CanMEDS 2025의 버추어 케어(Can Med Educ J. 2023) (0) | 2024.01.20 |
| CanMEDS 2025의 임상학습환경 (Can Med Educ J. 2023) (0) | 2024.01.20 |