프로그램 평가: 시작하기 그리고 기준(J Grad Med Educ, 2020)
Program Evaluation: Getting Started and Standards
Dorene F. Balmer, PhD (@dorenebalmer)
Janet M. Riddle, MD (@JanetRiddleDME)
Deborah Simpson, PhD (@debsimpson3)

더 챌린지
The Challenge
PD 및 기타 대학원 의학 교육(GME)1 교육자는 정기적으로 교육 프로그램을 평가한 후 유지, 개선 또는 중단해야 할 사항에 대한 판단을 내린다. 일부는 마치 연구처럼 프로그램 평가에 참여할 수 있다. 이는 놀랄 일이 아니다. 교수진은 품질 개선이나 연구 활동에 초점을 맞춘 체계적인 질의 훈련을 받으며, 이는 다른 목적에 기여하며 프로그램 평가와 비교하여 다양한 가정과 의도된 결과를 가지고 있다. 결과적으로, 프로그램 평가의 기본 가정, 목표/의도 결과, 방법 및 보고에 대한 교수진의 이해는 종종 제한적이며 어려운 논의로 이어진다.
PDs and other graduate medical education (GME)1 educators routinely evaluate their educational programs and then make judgments about what to keep, improve, or discontinue. Some may engage in program evaluation as if it were research. This is not surprising: faculty are trained in systematic inquiry focused on quality improvement or research activities, which serve different purposes and have varying assumptions and intended outcomes as compared with program evaluation. As a result, the faculty’s grasp of program evaluation’s underlying assumptions, aims/intended outcomes, methods, and reporting is often limited and leads to difficult discussions.
알려진 것
What Is Known
20세기 중반에 프로그램 평가는 그 분야로 발전했다. 오늘날 프로그램 평가의 목적은 대체로 다음의 두 가지 중 하나이다.
- (1) 교육 프로그램의 전체 가치 또는 가치를 결정하기 위한 데이터 사용(프로그램의 총괄적 판단) 또는
- (2) 프로그램 개선 계획(프로그램, 프로젝트 또는 활동의 형성적 개선)
오리엔테이션에 관계없이 프로그램 평가는 GME의 품질을 향상시킬 수 있으며, 궁극적으로는 더 나은 관리 품질을 통해 일반인에 대한 책임을 개선할 수 있다.
In the mid-20th century, programevaluation evolved into its own field. Today, the purpose of program evaluation typically falls in 1 of 2 orientations in using data to
- (1) determine the overall value or worth of an education program (summative judgements of a program) or
- (2) plan program improvement (formative improvements to a program, project, or activity).
Regardless of orientation, program evaluation can enhance the quality of GME and may ultimately improve accountability to the public through better quality of care.
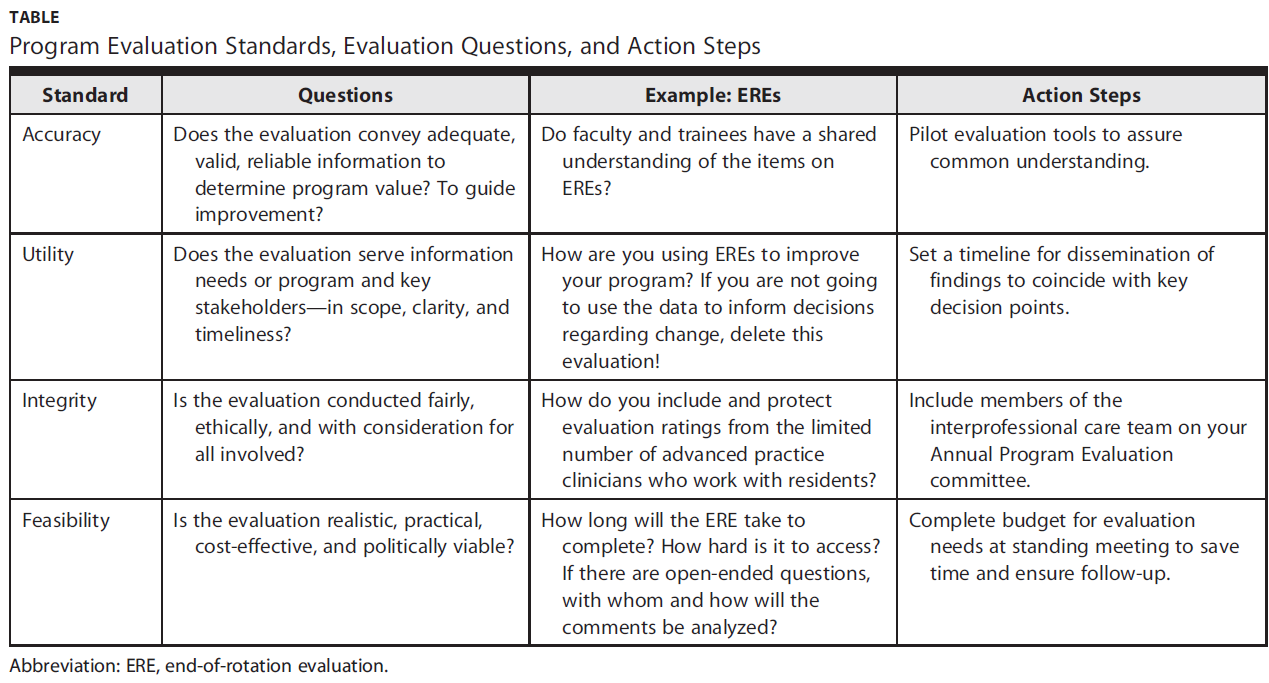
프로그램 평가 표준은 평가 품질을 보장하는 데 도움이 된다.2 PD와 GME 교육자는 정확성accuracy 하나에만 집중하는 경향이 있다. 그들은 프로그램 평가와 관련된 다른 표준, 즉 효용, 무결성(다양한 이해관계자에 대한 공정성) 및 실현 가능성을 고려하는 경우가 적다.
Program evaluation standards help to ensure the quality of evaluations.2 PDs and GME educators tend to focus on only one of these standards: accuracy. Less often, they consider the other standards associated with program evaluation: utility, integrity (fairness to diverse stakeholders), and feasibility.
지금 바로 시작하는 방법
How You Can Start TODAY
1. 평가 기준을 적용합니다. 이 표준은 평가에 대한 모든 논의에 적용되어야 하며, 진행 상황, 프로세스 및 결과의 무결성을 보장해야 합니다.
1. Apply the evaluation standards.The standards should be applied to every evaluation discussion—to assure the integrity of your progress, process, and outcomes.
2. 평가의 목적을 명확히 한다. 당신이 무엇을 평가하고 있고 왜 그런지 분명히 하세요.
- 교육 프로그램의 명시된 목표가 지역사회의 요구와 일치하는지 아니면 후원 기관의 임무와 일치하는지 평가하고 있는가?
- 당신은 외래 환경에서 학습 환경을 개선하는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니까?
2. Clarify the purpose of the evaluation.Be clear on what you are evaluating and why.
- Are you evaluating if the stated goals of the educational program are consistent with the needs of the community or the mission of the sponsoring institution?
- Are you aiming to improve the learning environment in ambulatory settings?
3. 항상 실행 가능성과 유용성에 대해 조기에 논의합니다. 그것은 멋진 접근법이 될 수 있지만 불가능할 수 있다! 평가 비용과 정치를 간과하지 마십시오. 데이터 수집을 시작하기 전에 실제로 정보를 어떻게 사용할 것인지, 그리고 누가 이 결과에 액세스할 수 있는지 확실히 알아야 합니다.
3. Always discuss feasibility and utility early on.It can be an awesome approach but impossible to do! Donot overlook the cost and politics of evaluation. Before you begin to collect your data, be clear abouthow you will actually use the information and who will have access to the findings.
4. 여러 이해 관계자를 고려하십시오. 대부분의 평가에서 교육생과 교직원은 핵심 이해 관계자이다. 환자, 커뮤니티 구성원, 병원, 의료 기관 및 품질 및 안전 위원회의 리더십도 교육 프로그램에 참여할 수 있습니다.
4. Consider multiple stakeholders. For most evaluations, trainees and faculty members are key stake-holders. Patients, community members, and leadership from your hospitals, clinics, and quality andsafety committees may also have a stake ineducational programs.
장기적으로 할 수 있는 일
What You Can Do LONG TERM
1. 작업 그룹을 소집합니다. 연례 프로그램 평가 위원회(또는 유사한 그룹)를 소집하고 우선 순위가 높은 결정을 검토합니다. 평가 표준을 적용하고 모든 기여자의 정보에 입각한 결정을 내릴 수 있는 정보가 충분하고 정확한지 판단합니다.
1. Convene your workgroup. Convene your Annual Program Evaluation committee (or similar group)and review high-priority decisions. Apply the evaluation standards and determine if you havesufficient and accurate information to make in-formed decisions from all contributors.
2. 채택, 적용, 작성. 자신의 평가 도구를 작성하기 전에 목표에 맞는 기존 평가 도구를 채택하거나 조정할 수 있다. 이상적인 상황에서, 이러한 도구는 이미 검사되었으므로, 비교 데이터를 제공할 수 있습니다.
2. Adopt, adapt, author. Adopt or adapt existing evaluation tools that align with your aim before authoring your own. Optimally, these tools have been vetted and can provide comparison data.
3. 익숙해지세요. 평가 및 평가 자원 분야(예: 미국 평가 협회)와 건강 전문가 교육의 프로그램 평가 리소스에 대해 알아봅니다.2,3
3. Familiarize yourself. Learn about the field of evaluation and evaluation resources (eg, American Evaluation Association) as well as program evaluation resources in health professions education.2,3
J Grad Med Educ. 2020 Jun;12(3):345-346.
doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-20-00265.1.
Program Evaluation: Getting Started and Standards
Dorene F Balmer, Janet M Riddle, Deborah Simpson
PMID: 32595857
PMCID: PMC7301948 (available on 2021-06-01)
'Articles (Medical Education) > 교육과정 개발&평가' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 의학교육은 정보시대에서 인공지능시대로 가야 한다(Acad Med, 2018) (0) | 2021.03.13 |
|---|---|
| 역할 기반 역량 모델에서 '잃어버린 사람': 역사, 국가 간, 비교 사례 연구(Med Educ, 2014) (0) | 2021.02.26 |
| 의사를 위한 CME활동에서의 기획 및 평가의 개념 프레임워크(Med Teach, 2018) (0) | 2021.02.05 |
| 위계적이지 않은 선형적 교육 이니셔티브 평가: 7I 프레임워크(J Educ Eval Health Prof, 2015) (0) | 2021.02.05 |
| 영국 기본의학교육에서 핵심 의사소통 커리큘럼의 합의문(Patient Educ Couns. 2018) (0) | 2021.02.05 |